 See all blog posts
See all blog posts
Simplify your runtime configuration with versionless features in 24.0.0.8-beta
This release simplifies choosing compatible features for the MicroProfile, Jakarta EE, and Java EE platforms by introducing versionless features. It also includes previews of Jakarta EE 11 and MicroProfile 7.0 beta features and a partitioned cookies function.
The Open Liberty 24.0.0.8-beta includes the following beta features (along with all GA features):
MicroProfile 7.0 beta features:
-
Enable the full set of MicroProfile 7.0 beta features with the MicroProfile 7.0 convenience feature
-
Integrate fault tolerance and OpenTelemetry with MicroProfile Fault Tolerance 4.1
-
Document APIs in OpenAPI 3.1 format with MicroProfile OpenAPI 4.0
-
Align your REST client with Jakarta RESTful Web Services with MicroProfile Rest Client 4.0
-
Collect and export HTTP metrics and logs with MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0
Jakarta EE 11 beta features:
See also previous Open Liberty beta blog posts.
Streamline feature selection with versionless Jakarta EE and MicroProfile features
With Open Liberty, you configure only the features at the specific versions that your application needs. This composable design pattern minimizes runtime resource requirements and accelerates application startup times. However, you might not always know which version of a feature is compatible with the rest of your application configuration. Determining the correct version typically requires a mix of experimentation, guesswork, and digging deep into feature documentation. Versionless features automate version selection, enabling you to focus on application development without worrying about compatibility issues.
Versionless features provide a generic way to specify Open Liberty features without having to specify a feature version. These new features are available for the MicroProfile, Jakarta EE, and Java EE platforms. When you use versionless features, you must specify a corresponding versioned platform element in your server.xml file.
For example, instead of specifying servlet-6.0 in your server.xml file and having to figure out which other feature versions are compatible with Servlet 6.0, you can specify a platform version and servlet. The platform that you specify resolves all versionless features to a compatible version.
The following server.xml file configuration uses a Java EE platform of javaee-8.0 with associated versionless features that are defined for servlet, jpa, and jaxrs:
Another example is specifying
<!-- Enable features -->
<featureManager>
<platform>javaee-8.0</platform>
<feature>servlet</feature>
<feature>jpa</feature>
<feature>jaxrs</feature>
</featureManager>This example enables versionless MicroProfile features with microProfile-5.0 specified as the platform element:
<!-- Enable features -->
<featureManager>
<platform>microProfile-5.0</platform>
<feature>mpHealth</feature>
<feature>mpMetrics</feature>
</featureManager>Check out the full collection of available platforms and versionless features in the lists at the end of this post. Stay tuned for more information about versionless features in a forthcoming blog post and full documentation when versionless features are released for general availability (GA).
Known limitations
-
Error handling scenarios return generic messages.
-
Feature installation scenarios that use command-line tools, including Maven and Gradle plug-ins, are not supported.
Keep using third party cookies with CHIPS
To increase privacy and reduce tracking, Google Chrome announced it would phase out third-party cookies in 2025. Then, as of July 22, 2024, Chrome stated they might scrap the phase-out plan due to regulatory concerns. Users instead could opt to block third party cookies via their browser. Some sites that are designed with third-party cookies in mind are broken by browsers that opt-in to block third party cookies. Chrome provides documentation to help you test whether your sites are affected. If you are, one option to mitigate this change is called CHIPS: Cookies Having Independent Partitioned State.
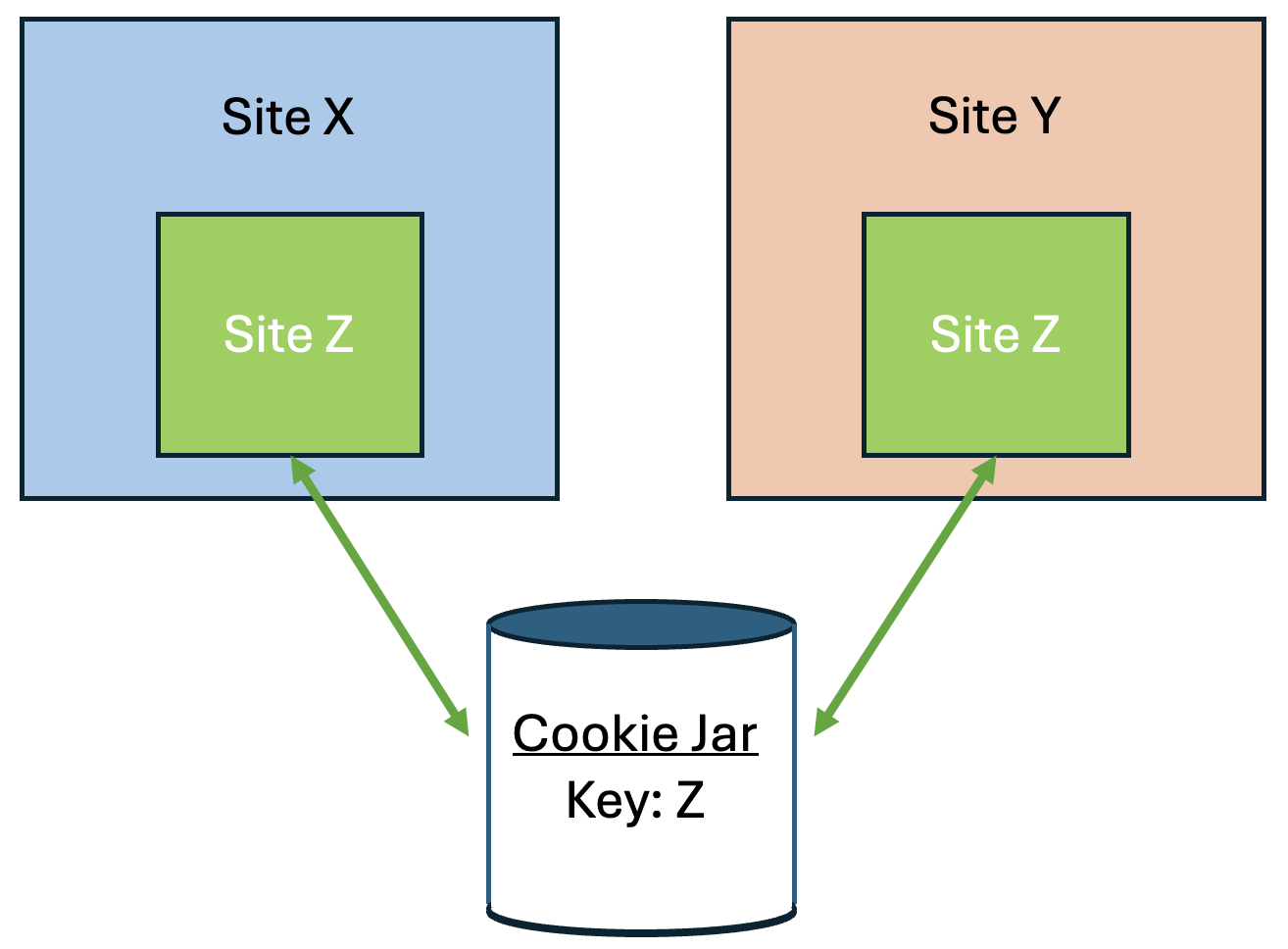
First, some background information regarding third-party (cross-site) cookies.
If a top-level site X embeds another site Z, such as an iframe, then any cookies set by the embedded site Z might be shared with any other site that embeds site Z, such as top-level site Y. This vulnerability is due to cookies placed in a cookie jar under the Z site key. This scenario assumes that the cookie is labeled as SameSite=None, because it isn’t shared when set to Lax or Strict.
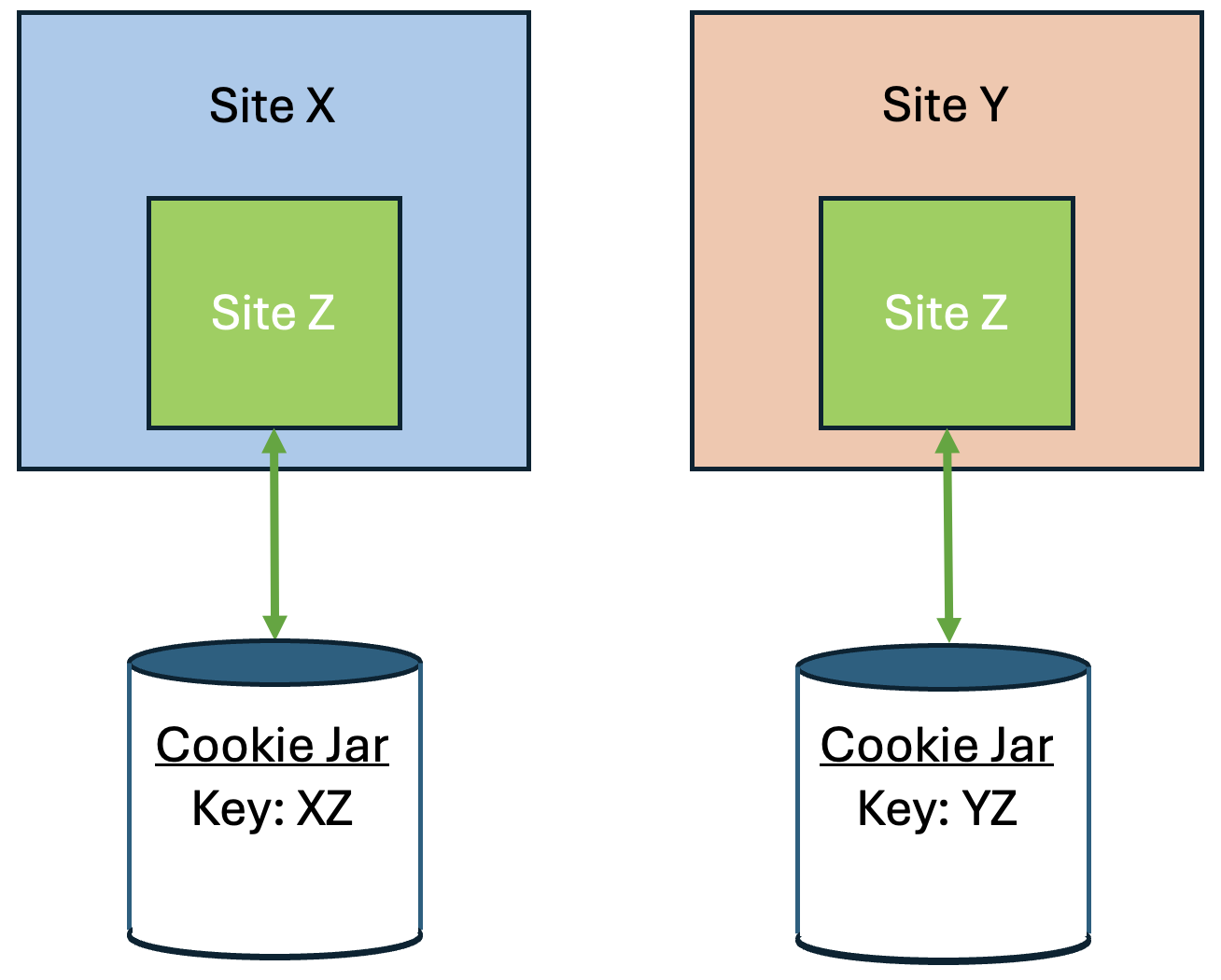
Chrome provides a Partitioned cookie attribute, which divides the cookie jar, as a workaround for third-party cookies with limitations. Instead of saving the cookies within the Z site key, they will also be keyed under the top-level site, such as X and Y. In this way, if X embeds Z and Y embeds Z, the Z’s cookies will not be shared between X and Y.
You can use the Partitioned attribute to specify whether a cookie is partitioned. If the SameSite=None attribute is missing from the cookie, it is blocked by Chrome and any Chromium-based browsers because it is treated as Lax.
The partitioned attribute configuration is opt-in and behaves much like the SameSite configuration. The samesite channel configuration applies to all cookies, while the httpSession and webAppSecurity configurations apply to their respective cookies. It’s important to note that the httpSession and webAppSecurity configurations take precedence over the channel configuration. The default value for these two attributes is defer, which means they defer to the channel configuration. As for channel configuration, its default value is false, which means the Partitioned attribute is not added.
Depending on which configuration you use to declare the Partitioned attribute, Liberty uses one of three attributes.
The following example shows how to set the cookiePartitioned attribute for the HTTP session cookie on the httpSession attribute in your server.xml file:
<httpSession cookieSameSite="None" cookiePartitioned="defer|true|false"/>`The following example shows how to set the partitionedCookie attribute for LTPA and JWT security cookies on the webAppSecurity attribute in your server.xml file:
<webAppSecurity sameSiteCookie="None" partitionedCookie="defer|true|false"/>`The following example shows how to set the partitioned attribute for other cookies on the httpEndpoint attribute in your server.xml file:
<httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint"
httpPort="9080"
httpsPort="9443" >
<samesite none="*" partitioned="true|false"/>
</httpEndpoint>Alternatively, you can set Partitioned by using the Set-Cookie header with the following two HttpServletResponse APIs:
For more information, including a visual example, see CHIPS (Cookies Having Independent Partitioned State) on GitHub.
Enable the full set of MicroProfile 7.0 beta features with the MicroProfile 7.0 convenience feature
The 24.0.0.8-beta release includes the beta release of MicroProfile 7.0 and the microProfile-7.0 convenience feature.
MicroProfile 7.0 (MP 7.0) is a major release. It brings in Jakarta EE 10 and Jakarta 11 core profile APIs and the following MicroProfile component specifications:
The following 4 specifications have updates while the other 3 specifications remain unchanged.
MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 now provides support for OpenTelemetry logs and metrics. Consequently, MicroProfile Metrics is not part of MicroProfile 7.0. However, the MicroProfile Metrics 5.1 feature is still compatible with MicroProfile 7.0 features.
To enable MicroProfile 7.0 and all its constituent features, add the microProfile-7.0 convenience feature to your server.xml file:
<featureManager>
<feature>microProfile-7.0</feature>
</featureManager>Integrate fault tolerance and OpenTelemetry with MicroProfile Fault Tolerance 4.1
MicroProfile Fault Tolerance helps you easily identify and mitigate failures in your code. It provides annotations that you can add to methods to use bulkhead, circuit breaker, retry, timeout, and fallback strategies.
The new mpFaultTolerance-4.1 feature integrates with the mpTelemetry-2.0 feature, so that Fault Tolerance can export metric data to OpenTelemetry. With this change, and other changes in mpTelemetry-2.0, you can simplify the configuration and management of your application observability by using OpenTelemetry as the single source for logging, metrics, and tracing.
To enable this functionality, enable mpFaultTolerance-4.1 and mpTelemetry-2.0 in your server.xml file and then configure mpTelemetry-2.0 to export metrics. The following examples show a minimal configuration for OpenTelemetry to export to your messages.log file and a class that generates Fault Tolerance metrics (it must be accessed as a CDI bean).
server.xml file configuration
<featureManager>
<feature>mpFaultTolerance-4.1</feature>
<feature>mpTelemetry-2.0</feature>
</featureManager>bootstrap.properties file configuration
The following example configures OpenTelemetry to only output metrics to the messages.log file.
It also sets a very low interval for exporting metrics so you can see the results quickly.
otel.sdk.disabled=false
otel.metrics.exporter=logging
otel.logs.exporter=none
otel.traces.exporter=none
otel.metric.export.interval=500Example application class
Ensure that this class is injected as a CDI bean and invoked by the user in whatever way you prefer.
import org.eclipse.microprofile.faulttolerance.Retry;
import jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped;
@ApplicationScoped
public class ExampleClass {
@Retry
public int exampleMethod(String name) {
return 1;
}
}Learn more
You can read more details about the changes in the new version in the Microprofile Fault Tolerance 4.1 RC2 specification and API Javadoc.
You can learn more about how to use MicroProfile Fault Tolerance from our documentation and guides.
Document APIs in OpenAPI 3.1 format and more with MicroProfile OpenAPI 4.0
OpenAPI is a standardized way to document REST APIs in a JSON or YAML format. MicroProfile OpenAPI helps you generate and serve OpenAPI documentation for your REST applications that are built using JAX-RS or Jakarta RESTful Web Services. This documentation is useful for developers to test out the API during development, or for people using the API in production.
With the new MicroProfile OpenAPI 4.0 feature (mpOpenAPI-4.0), documentation is now produced in OpenAPI 3.1 format, updated from 3.0 in previous versions. Changes in OpenAPI 3.1 include:
-
Use of full JSON Schema 2020-12 draft for data object schemas (updated from a subset of an older JSON schema draft in 3.0)
-
Support for documenting webhooks
-
Reusable PathItems
-
Updates to the model API so that it directly reflects the OpenAPI 3.1 format
-
Additions to the annotations API to allow users to take advantage of the new features of OpenAPI 3.1
A detailed list of changes can be found in the release notes of the specification.
This is an early beta release to support the ratification of MicroProfile 7.0. As such, some function which was available in previous versions of the feature are not yet implemented:
-
Documenting more than one web module as can be configured in previous versions
-
Validation of the produced OpenAPI document
Learn more
For more information, see the following resources:
Align your REST client with Jakarta RESTful Web Services with MicroProfile Rest Client 4.0
MicroProfile Rest Client provides a type-safe approach to invoke RESTful services over HTTP. As much as possible, the MicroProfile Rest Client 4.0 release attempts to use Jakarta RESTful Web Services 3.1 APIs for consistency and easier re-use.
The MicroProfile Rest Client 4.0 feature (mpRestClient-4.0) aligns with Jakarta RESTful Web Services 3.1 as part of the greater effort to align MicroProfile 7.0 with Jakarta EE10. The beta release of this feature includes the following updates:
-
Added a new
RestClientBuilder.header(String, Object)method to add dynamic headers to the request. -
Added a new
RestClientBuilder.baseUri(String)overload method so users don’t have to callURI.create(String). -
Added clarification in the spec on how to use Jakarta RESTful Web Services
EntityPartAPI for multipart requests.
Learn more
For more information, see the following resources:
Collect and export HTTP metrics and logs with MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0
MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 (mpTelemetry-2.0) provides developers with the latest OpenTelemetry technology. The feature now consumes OpenTelemetry-1.34.0. In addition to distributed tracing, the feature now allows OpenTelemetry to collect and export HTTP metrics and logs.
To enable the mpTelemetry-2.0 feature to collect metrics, logs, and traces, add the following configuration to your server.xml file:
<featureManager>
<feature>mpTelemetry-2.0</feature>
</featureManager>Additionally, you must add the following configuration to your server.xml file to make third-party APIs visible for your application:
<webApplication location="application-name.war" contextRoot="/">
<!-- enable visibility to third party apis -->
<classloader apiTypeVisibility="+third-party"/>
</webApplication>HTTP Metrics
In the 24.0.0.7-beta release, we introduced Enhanced HTTP Request Monitoring with Monitor 1.0. This update enables you to track HTTP requests made to the server and record the following data:
-
Request method
-
Response status
-
Duration
-
HTTP route
-
Other attributes that align with the OpenTelemetry HTTP metric semantic conventions.
This information is recorded into an HttpStatsMXBean. If the MicroProfile Metrics 5.0 or later feature (mpMetrics-5.x) is enabled, then the HTTP metrics are reported on the /metrics REST endpoint.
In this beta release, we can now register HTTP Metrics with the mpTelemetry-2.0 feature. This metric data can then be exported to a compatible OpenTelemetry metrics consumer. This enhancement is an auto-feature that activates with mpTelemetry-2.0, monitor-1.0, and any feature that uses the servlet engine that currently supports Jakarta EE 10 features, such as servlet-6.0, pages-3.1, and restfulWS-3.1.
Logs
Logs generated by the java.util.logging (JUL) package and message logs can now be collected by OpenTelemetry with the mpTelemetry-2.0 feature.
To collect and export runtime-level logs and metrics, enable OpenTelemetry by using the following system property or environment variable:
-
System property:
otel.sdk.disabled=false -
Environment variable:
OTEL_SDK_DISABLED=false
To separately configure for multiple applications on a server, you can configure OpenTelemetry at the application level. However, you cannot collect runtime-level logs and metrics with this configuration.
By default, all OpenTelemetry data is exported to the OTLP. You can change each exporter with the following system properties and variables.
System properties:
-
otel.metrics.exporter -
otel.logs.exporter -
otel.traces.exporter
Environment variables:
-
OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER -
OTEL_LOGS_EXPORTER -
OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER
MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 beta known issues
Tracing context is not transferred through threads in REST Client async requests. Therefore, context values are inconsistent with parent and child spans.
Bring your own Jakarta Data provider with Jakarta Data API 1.0
Jakarta Data 1.0 is a new Jakarta EE specification that standardizes a repository-based programming model for data access across relational and non-relational databases.
The Jakarta Data API feature (dataContainer-1.0) enables you to use third-party Jakarta Data providers in Open Liberty without including the built-in provider for EclipseLink. This configuration is useful if you want to use a different Jakarta Persistence-based Jakarta Data provider, such as Hibernate, without colliding on the Jakarta Persistence Entity annotation. It’s also useful if you want to use Jakarta NoSQL exclusively and do not want the overhead of the built-in provider for relational databases.
To use a third-party Jakarta Data provider, enable the dataContainer-1.0 feature in your server.xml file. You can then include a third-party Jakarta Data provider in your server configuration by using the library element.
The following server.xml file example shows the configuration to use the Eclipse jNoSQL Jakarta Data provider and a MongoDB database:
<featureManager>
<feature>dataContainer-1.0</feature>
<!-- Features needed for jNoSQL config / processing -->
<feature>mpConfig-3.1</feature>
<feature>jsonb-3.0</feature>
</featureManager>
<library id="jnosql">
<!-- Jakarta NoSQL API -->
<fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/nosql" includes="jakarta.nosql-api.jar" />
<!-- Eclipse jNoSQL Implementation of Jakarta NoSQL and Jakarta Data -->
<fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/jnosql"
includes="jnosql-communication-core.jar jnosql-mapping-core.jar jnosql-mongodb.jar *.jar" />
<!-- Mongo java driver -->
<fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/mongodb"
includes="mongodb-driver-core.jar mongodb-driver-sync.jar" />
</library>
<!-- MongoDB connection configuration -->
<variable name="jnosql.mongodb.host" value="${MONGO_HOST}"/>
<variable name="jnosql.document.database" value="${MONGO_DBNAME}"/>
<application location="MyApplication.war">
<classloader commonLibraryRef="jnosql" />
</application>To use a third-party Jakarta Persistence-based Jakarta Data provider, include the dataContainer-1.0 and persistenceContainer-3.2 features. You can then include the third-party Jakarta Data provider in your server configuration by using a library element.
The following server.xml file example shows the configuration to use the Hibernate ORM Jakarta Data provider and a PostgreSQL database:
<featureManager>
<feature>dataContainer-1.0</feature>
<feature>persistenceContainer-3.2</feature>
<!-- Features needed for Hibernate config / processing -->
<feature>xmlBinding-4.0</feature>
</featureManager>
<!-- Hibernate Implementation of Jakarta Persistence and Jakarta Data -->
<library id="hibernate">
<fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/hibernate"
includes="hibernate-core.jar hibernate-models.jar *.jar"/>
</library>
<!-- PostgreSQL JDBC driver -->
<library id="postgresql">
<fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/postgresql" includes="*.jar"/>
</library>
<!-- Datasource used to create a Persistence Unit -->
<dataSource jndiName="jdbc/postgresql" >
<jdbcDriver libraryRef="postgresql"/>
<properties.postgresql URL="${POSTGRESQL_URL}"/>
</dataSource>
<application location="MyApplication.war">
<classloader commonLibraryRef="hibernate, postgresql" />
</application>Hibernate ORM uses a persistence unit to persist entities that are defined on a Jakarta Data repository interface. To create a persistence unit, add a META-INF/persistence.xml deployment descriptor file to your application, similar to the following example.
<persistence xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_3_2.xsd"
version="3.2">
<persistence-unit name="postgresql-pu">
<provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider</provider>
<jta-data-source>jdbc/postgresql</jta-data-source>
<properties>
<property name="jakarta.persistence.schema-generation.database.action" value="create"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>Learn more
For more information, see the following resources:
Bring your own Jakarta Faces implementation with Jakarta Faces Container 4.1
Jakarta Faces is a Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework for building web applications. It offers many convenient features, such as state management and input validation.
The Jakarta Faces Container 4.1 feature (facesContainer-4.1) enables you to bring your own Jakarta Faces API and implementation to Liberty. The alternative is to use the Liberty-provided faces-4.1 feature, which provides the MyFaces 4.1 API and implementation.
The Faces Container feature is updated in this beta release to support the 4.1 API and implementation JARs. If the 4.1 JARs were used with earlier features, errors occurred because the feature checks against the specification version listed within the jars.
To use the facesContainer-4.1 feature, add the following configuration to your server.xml file:
<featureManager>
<feature>facesContainer-4.1</feature>
</featureManager>Learn more
For more information, see the following resources:
Improve asynchronous handling with Jakarta WebSocket 2.2
The Jakarta WebSocket 2.2 (websocket-2.2) feature enables communication for endpoints by using the WebSocket protocol. It is an implementation of the Jakarta EE 11 WebSocket 2.2 Specification.
Although very few specification changes were listed for the 2.2 release, the main change from 2.1 is the introduction of the getSession() method on the SendResult class. This method enables you to retrieve the original session that was used in the asynchronous remote call. This capability is useful for broadcasting messages to numerous listening clients.
To enable this feature, add the following configuration to your server.xml file.
<featureManager>
<feature>websocket-2.2</feature>
</featureManager>Learn more
For more information, such as the Javadocs, specification documents, and other details, see the Jakarta WebSocket 2.2 specification document and Send bidirectional messages between services with WebSocket in the Open Liberty docs.
Use Jakarta Persistence with improved type safety and other enhancements with Jakarta Persistence 3.2
The Jakarta Persistence feature (persistence-3.2) provides an object-model approach to persist, fetch, and modify data that is stored on a relational database system.
Jakarta Persistence 3.2 includes the following updates:
-
Improve type safety of the
find()andrefresh()methods -
Provide schema management programmatically
-
Allow Java records as embeddable types
-
Add functions and operators to the JPQL/Criteria API, such as
left,right,replace,||operator,cast,union,union all,intersect,intersect all,except, andexcept all -
Support for subqueries in the
select,from, andjoinclauses.
To use the persistence-3.2 feature, add the following configuration to your server.xml file:
<featureManager>
<feature>persistence-3.2</feature>
</featureManager>This feature uses Eclipselink 5.0 beta release as the Jakarta Persistence provider. To bring your own 3rd party persistence provider, enable the persistenceContainer-3.2 feature instead:
<featureManager>
<feature>persistenceContainer-3.2</feature>
</featureManager>Learn more
For more information, see the Data persistence with the Jakarta Persistence API in the Open Liberty docs and the Jakarta Persistence 3.2 specification document.
Try it now
To try out these features, update your build tools to pull the Open Liberty All Beta Features package instead of the main release. The beta works with Java SE 22, Java SE 21, Java SE 17, Java SE 11, and Java SE 8. However, Java SE 17 or later is required for the Jakarta EE 11 features that are in the beta.
If you’re using Maven, you can install the All Beta Features package using:
<plugin>
<groupId>io.openliberty.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>liberty-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.10.3</version>
<configuration>
<runtimeArtifact>
<groupId>io.openliberty.beta</groupId>
<artifactId>openliberty-runtime</artifactId>
<version>24.0.0.8-beta</version>
<type>zip</type>
</runtimeArtifact>
</configuration>
</plugin>You must also add dependencies to your pom.xml file for the beta version of the APIs that are associated with the beta features that you want to try. For example, the following block adds dependencies for two example beta APIs:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example.spec</groupId>
<artifactId>exampleApi</artifactId>
<version>7.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>example.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>example.example-api</artifactId>
<version>11.0.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>Or for Gradle:
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'io.openliberty.tools:liberty-gradle-plugin:3.8.3'
}
}
apply plugin: 'liberty'
dependencies {
libertyRuntime group: 'io.openliberty.beta', name: 'openliberty-runtime', version: '[24.0.0.8-beta,)'
}Or if you’re using container images:
FROM icr.io/appcafe/open-liberty:betaOr take a look at our Downloads page.
If you’re using IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio Code or Eclipse IDE, you can also take advantage of our open source Liberty developer tools to enable effective development, testing, debugging and application management all from within your IDE.
For more information on using a beta release, refer to the Installing Open Liberty beta releases documentation.
We welcome your feedback
Let us know what you think on our mailing list. If you hit a problem, post a question on StackOverflow. If you hit a bug, please raise an issue.
Platforms and related versionless features reference list
The following platform features are available in this beta release. You can specify up to 2 platform elements, one for MicroProfile, another for either Jakarta EE or Java EE.
MicroProfile
Platforms
-
microProfile-1.2 -
microProfile-1.3 -
microProfile-1.4 -
microProfile-2.0 -
microProfile-2.1 -
microProfile-2.2 -
microProfile-3.0 -
microProfile-3.2 -
microProfile-3.3 -
microProfile-4.0 -
microProfile-4.1 -
microProfile-5.0 -
microProfile-6.0 -
microProfile-6.1 -
microProfile-7.0
Versionless features
-
mpConfig -
mpFaultTolerance -
mpHealth -
mpJwt -
mpMetrics -
mpOpenAPI -
mpOpenTracing -
mpRestClient -
mpTelemetry
Jakarta EE and Java EE
Platforms
-
javaee-7.0 -
javaee-8.0 -
jakartaee-9.1 -
jakartaee-10.0 -
jakartaee-11.0
Versionless features
Although Liberty uses different feature names and short names for some Java EE and Jakarta EE versions of the same feature, you can use either short name and the platform you specify pulls in the correct compatible feature.
-
appAuthenticationorjaspic -
appAuthorizationorjacc -
appClientSupport -
appSecurity -
batch -
beanValidation -
cdi -
concurrent -
connectorsorjca -
connectorsInboundSecurityorjcaInboundSecurity -
data -
enterpriseBeansorejb -
enterpriseBeansHomeorejbHome -
enterpriseBeansLiteorejbLite -
enterpriseBeansPersistentTimerorejbPersistentTimer -
enterpriseBeansRemoteorejbRemote -
expressionLanguageorel -
facesorjsf -
j2eeManagement -
jdbc -
jsonb -
jsonp -
mailorjavaMail -
managedBeans -
mdb -
messagingorjms -
messagingClientorwasJmsClient -
messagingSecurityorwasJmsSecurity -
messagingServerorwasJmsServer -
pagesorjsp -
persistenceorjpa -
restfulWSorjaxrs -
restfulWSClientorjaxrsClient -
servlet -
websocket -
xmlBindingorjaxb -
xmlWSorjaxws




