
Contents
- What you’ll learn
- Additional prerequisites
- Getting started
- Getting started with Liberty and REST
- Documenting APIs
- Configuring the microservice
- Persisting data
- Securing RESTful APIs
- Consuming the secured RESTful APIs by JWT
- Adding health checks
- Providing metrics
- Building the container
- Testing the microservice with Testcontainers
- Starting and preparing your cluster for deployment
- Deploying the microservice to Kubernetes
- Support Licensing
- Great work! You’re done!
- Guide Attribution
Tags

A Technical Deep Dive on Liberty
Prerequisites:
Liberty is a cloud-optimized Java runtime that is fast to start up with a low memory footprint and a dev mode, for quick iteration. With Liberty, adopting the latest open cloud-native Java APIs, like MicroProfile and Jakarta EE, is as simple as adding features to your Liberty configuration. The Liberty zero migration architecture lets you focus on what’s important and not the APIs changing under you.
What you’ll learn
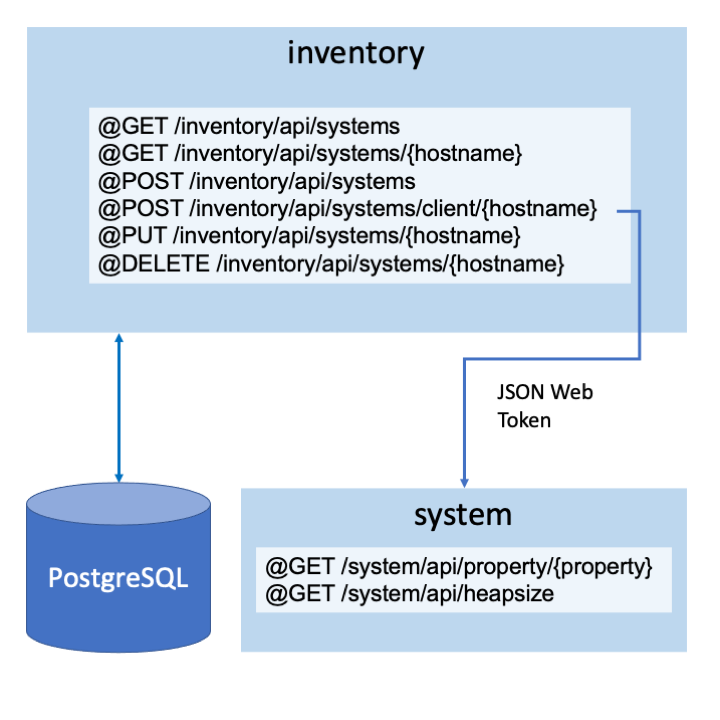
You will learn how to build a RESTful microservice on Liberty with Jakarta EE and MicroProfile. You will use Gradle throughout this exercise to build the microservice and to interact with the running Liberty instance. Then, you’ll build a container image for the microservice and deploy it to Kubernetes in a Liberty Docker container. You will also learn how to secure the REST endpoints and use JSON Web Tokens to communicate with the provided system secured microservice.
The microservice that you’ll work with is called inventory. The inventory microservice persists data into a PostgreSQL database.

Additional prerequisites
Podman must be installed before you start the Persisting Data module. For installation instructions, refer to the official Podman documentation. You will build and run the microservices in containers.
If you are running Mac or Windows, make sure to start your Podman-managed VM before you proceed.
Also, if you are using Linux, Kubernetes must be installed before you start the Deploying the microservice to Kubernetes.
You will use Minikube as a single-node Kubernetes cluster that runs locally in a virtual machine. Make sure that you have kubectl installed. If you need to install kubectl, see the kubectl installation instructions.
For Minikube installation instructions, see the Minikube documentation.
Getting started
Clone the Git repository:
git clone https://github.com/openliberty/guide-liberty-deep-dive-gradle.git
cd guide-liberty-deep-dive-gradleThe start directory is an empty directory where you will build the inventory service.
The finish directory contains the finished projects of different modules that you will build.
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary prerequisites.
Getting started with Liberty and REST
Liberty now offers an easier way to get started with developing your application: the Open Liberty Starter. This tool provides a simple and quick way to get the necessary files to start building an application on Liberty. Through this tool, you can specify your application and project name. You can also choose a build tool from either Maven or Gradle, and pick the Java SE, Jakarta EE, and MicroProfile versions for your application.
In this workshop, the Open Liberty Starter is used to create the starting point of the application. Gradle is used as the selected build tool and the application uses of Jakarta EE 10 and MicroProfile 6.1.
To get started with this tool, see the Getting Started page: https://openliberty.io/start/
On that page, enter the following properties in the Create a starter application wizard.
-
Under Group specify:
io.openliberty.deepdive -
Under Artifact specify:
inventory -
Under Build Tool select:
Gradle -
Under Java SE Version select:
17 -
Under Java EE/Jakarta EE Version select:
10.0 -
Under MicroProfile Version select:
6.1
Then, click Generate Project, which downloads the starter project as inventory.zip file.
Next, extract the inventory.zip file on your system. Move the contents of this extracted inventory directory to the start directory of this project, which is at the following path: guide-liberty-deepdive-gradle/start/inventory.
Instead of manually downloading and extracting the project, run the following commands in the start directory:
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
curl -o inventory.zip 'https://start.openliberty.io/api/start?a=inventory&b=gradle&e=10.0&g=io.openliberty.deepdive&j=17&m=6.1'
Expand-Archive -Path .\inventory.zipcurl -o inventory.zip 'https://start.openliberty.io/api/start?a=inventory&b=gradle&e=10.0&g=io.openliberty.deepdive&j=17&m=6.1'
unzip inventory.zip -d inventoryBuilding the application
This application is configured to be built with Gradle. Every Gradle-configured project contains a settings.gradle and a build.gradle file that defines the project configuration, dependencies, and plug-ins.
settings.gradle
build.gradle
Your settings.gradle and build.gradle files are located in the start/inventory directory and is configured to include the io.openliberty.tools.gradle.Liberty Liberty Gradle plugin. Using the plug-in, you can install applications into Liberty and manage the associated Liberty instances.
To begin, open a command-line session and navigate to your application directory.
cd start/inventoryBuild and deploy the inventory microservice to Liberty by running the Gradle libertyRun goal:
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
gradlew libertyRun./gradlew libertyRunThe gradlew command initiates a Gradle build, during which the target directory is created to store all build-related files.
The libertyRun argument specifies the Liberty run goal, which starts a Liberty instance in the foreground. As part of this phase, a Liberty server runtime is downloaded and installed into the build/wlp directory. Additionally, a Liberty instance is created and configured in the build/wlp/usr/servers/defaultServer directory, and the application is installed into that Liberty instance by using loose config.
For more information about the Liberty Gradle plug-in, see its GitHub repository.
While the Liberty instance starts up, various messages display in your command-line session. Wait for the following message, which indicates that the instance startup is complete:
[INFO] [AUDIT] CWWKF0011I: The server defaultServer is ready to run a smarter planet.When you need to stop the Liberty instance, press CTRL+C in the command-line session where you ran the Liberty.
Starting and stopping the Liberty in the background
Although you can start and stop the Liberty instance in the foreground by using the Gradle libertyRun task, you can also start and stop the server in the background with the Gradle libertyStart and libertyStop goals:
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
gradlew libertyStart
gradlew libertyStop./gradlew libertyStart
./gradlew libertyStopUpdating the Liberty configuration without restarting the instance
The Liberty Gradle plug-in includes a dev goal that listens for any changes in the project, including application source code or configuration. The Liberty instance automatically reloads the configuration without restarting. This goal allows for quicker turnarounds and an improved developer experience.
If the Liberty instance is running, stop it and restart it in dev mode by running the libertyDev goal in the start/inventory directory:
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
gradlew libertyDev./gradlew libertyDevAfter you see the following message, your Liberty instance is ready in dev mode:
************************************************************** * Liberty is running in dev mode.
Dev mode automatically picks up changes that you make to your application and allows you to run tests by pressing the enter/return key in the active command-line session. When you’re working on your application, rather than rerunning Gradle commands, press the enter/return key to verify your change.
Developing a RESTful microservice
Now that a basic Liberty application is running, the next step is to create the additional application and resource classes that the application needs. Within these classes, you use Jakarta REST and other MicroProfile and Jakarta APIs.
Create theInventoryclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/Inventory.java
Inventory.java
This Inventory class stores a record of all systems and their system properties. The getSystem() method within this class retrieves and returns the system data from the system. The add() method enables the addition of a system and its data to the inventory. The update() method enables a system and its data on the inventory to be updated. The removeSystem() method enables the deletion of a system from the inventory.
Create the model subdirectory, then create the SystemData class. The SystemData class is a Plain Old Java Object (POJO) that represents a single inventory entry.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
mkdir src\main\java\io\openliberty\deepdive\rest\modelmkdir src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/modelCreate theSystemDataclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/model/SystemData.java
SystemData.java
The SystemData class contains the hostname, operating system name, Java version, and heap size properties. The various methods within this class allow the viewing or editing the properties of each system in the inventory.
Create theSystemResourceclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
RestApplication.java
In Jakarta RESTful Web Services, a single class like the SystemResource.java class must represent a single resource, or a group of resources of the same type. In this application, a resource might be a system property, or a set of system properties. It is efficient to have a single class handle multiple different resources, but keeping a clean separation between types of resources helps with maintainability.
The @Path annotation on this class indicates that this resource responds to the /systems path in the RESTful application. The @ApplicationPath annotation in the RestApplication class, together with the @Path annotation in the SystemResource class, indicates that this resource is available at the /api/systems path.
The Jakarta RESTful Web Services API maps the HTTP methods on the URL to the methods of the class by using annotations. This application uses the GET annotation to map an HTTP GET request to the /api/systems path.
The @GET annotation on the listContents method indicates that the method is to be called for the HTTP GET method. The @Produces annotation indicates the format of the content that is returned. The value of the @Produces annotation is specified in the HTTP Content-Type response header. For this application, a JSON structure is returned for these Get methods. The Content-Type for a JSON response is application/json with MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON instead of the String content type. Using a constant such as MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON is better as in case of a spelling error, a compile failure occurs.
The Jakarta RESTful Web Services API supports a number of ways to marshal JSON. The Jakarta RESTful Web Services specification mandates JSON-Binding (JSON-B). The method body returns the result of inventory.getSystems(). Because the method is annotated with @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON), the Jakarta RESTful Web Services API uses JSON-B to automatically convert the returned object to JSON data in the HTTP response.
Running the application
Because you started the Liberty in dev mode at the beginning of this exercise, all the changes were automatically picked up.
Check out the service that you created at the http://localhost:9080/inventory/api/systems URL. If successful, it returns [] to you.
Documenting APIs
Next, you will investigate how to document and filter RESTful APIs from annotations, POJOs, and static OpenAPI files by using MicroProfile OpenAPI.
The OpenAPI specification, previously known as the Swagger specification, defines a standard interface for documenting and exposing RESTful APIs. This specification allows both humans and computers to understand or process the functionalities of services without requiring direct access to underlying source code or documentation. The MicroProfile OpenAPI specification provides a set of Java interfaces and programming models that allow Java developers to natively produce OpenAPI v3 documents from their RESTful applications.
build.gradle
server.xml
The MicroProfile OpenAPI API is included in the microProfile dependency that is specified in your build.gradle file. The microProfile feature that includes the mpOpenAPI feature is also enabled in the server.xml configuration file.
Generating the OpenAPI document
Because the Jakarta RESTful Web Services framework handles basic API generation for Jakarta RESTful Web Services annotations, a skeleton OpenAPI tree can be generated from the existing inventory service. You can use this tree as a starting point and augment it with annotations and code to produce a complete OpenAPI document.
To see the generated OpenAPI tree, you can either visit the http://localhost:9080/openapi URL or visit the http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui URL for a more interactive view of the APIs. Click the interactive UI link on the welcome page. Within this UI, you can view each of the endpoints that are available in your application and any schemas. Each endpoint is color coordinated to easily identify the type of each request (for example GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.). Clicking each endpoint within this UI enables you to view further details of each endpoint’s parameters and responses. This UI is used for the remainder of this workshop to view and test the application endpoints.
Augmenting the existing Jakarta RESTful Web Services annotations with OpenAPI annotations
Because all Jakarta RESTful Web Services annotations are processed by default, you can augment the existing code with OpenAPI annotations without needing to rewrite portions of the OpenAPI document that are already covered by the Jakarta RESTful Web Services framework.
Replace theSystemResourcesclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
Add OpenAPI @APIResponseSchema, @APIResponses, @APIResponse, @Parameters, @Parameter, and @Operation annotations to the REST methods, listContents(), getSystem(), addSystem(), updateSystem(), removeSystem(), and addSystemClient().
Note, the @Parameter annotation can be placed either inline or outline. Examples of both are provided within this workshop.
Many OpenAPI annotations are available and can be used according to what’s best for your application and its classes. You can find all the annotations in the MicroProfile OpenAPI specification.
Because the Liberty was started in dev mode at the beginning of this exercise, your changes were automatically picked up. Go to the http://localhost:9080/openapi URL to see the updated endpoint descriptions. The endpoints at which your REST methods are served now more meaningful:
---
openapi: 3.0.3
info:
title: Generated API
version: "1.0"
servers:
- url: http://localhost:9080/inventory
- url: https://localhost:9443/inventory
paths:
/api/systems:
get:
summary: List contents.
description: Returns the currently stored host:properties pairs in the inventory.
operationId: listContents
responses:
"200":
description: Returns the currently stored host:properties pairs in the inventory.
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/SystemData'
...You can also visit the http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui URL to see each endpoint’s updated description. Click each of the icons within the UI to see the updated descriptions for each of the endpoints.
Augmenting POJOs with OpenAPI annotations
OpenAPI annotations can also be added to POJOs to describe what they represent. Currently, the OpenAPI document doesn’t have a meaningful description of the SystemData POJO so it’s difficult to tell exactly what this POJO is used for. To describe the SystemData POJO in more detail, augment the SystemData.java file with some OpenAPI annotations.
Replace theSystemDataclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/model/SystemData.java
SystemData.java
Add OpenAPI @Schema annotations to the SystemData class and the hostname variable.
Refresh the http://localhost:9080/openapi URL to see the updated OpenAPI tree. You should see much more meaningful data for the Schema:
components:
schemas:
SystemData:
description: POJO that represents a single inventory entry.
required:
- hostname
- properties
type: object
properties:
hostname:
type: string
properties:
type: objectAgain, you can also view this at the http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui URL. Scroll down in the UI to the schemas section and open up the SystemData schema icon.
You can also use this UI to try out the various endpoints. In the UI, head to the POST request /api/systems. This endpoint enables you to create a system. Once you’ve opened this icon up, click the Try it out button. Now enter appropriate values for each of the required parameters and click the Execute button.
You can verify that this system was created by testing the /api/systems GET request that returns the currently stored system data in the inventory. Execute this request in the UI, then in the response body you should see your system and its data listed.
You can follow these same steps for updating and deleting systems: visiting the corresponding endpoint in the UI, executing the endpoint, and then verifying the result by using the /api/systems GET request endpoint.
You can learn more about MicroProfile OpenAPI from the Documenting RESTful APIs guide.
Configuring the microservice
Next, you can externalize your Liberty configuration and inject configuration for your microservice by using MicroProfile Config.
Enabling configurable ports and context root
So far, you used hardcoded values to set the HTTP and HTTPS ports and the context root for the Liberty. These configurations can be externalized so you can easily change their values when you want to deploy your microservice by different ports and context root.
Replace the Libertyserver.xmlconfiguration file.src/main/liberty/config/server.xml
server.xml
Add variables for the HTTP port, HTTPS port, and the context root to the server.xml configuration file. Change the httpEndpoint element to reflect the new http.port and https.port variables and change the contextRoot to use the new context.root variable too.
Replace thebuild.gradlefile.build.gradle
build.gradle
Set the archiveVersion property to an empty string for the war task and add properties for the HTTP port, HTTPS port, and the context root to the build.gradle file.
-
liberty.var.http.portto9081 -
liberty.var.https.portto9445 -
liberty.var.context.rootto/trial
Because you are using dev mode, these changes are automatically picked up by the Liberty instance.
Now, you can access the application by the http://localhost:9081/trial/api/systems URL. Alternatively, for the updated OpenAPI UI, use the following URL http://localhost:9081/openapi/ui/.
build.gradle
1plugins {
2 id 'war'
3 // tag::libertyGradlePlugin[]
4 id 'io.openliberty.tools.gradle.Liberty' version '3.8.3'
5 // end::libertyGradlePlugin[]
6}
7
8version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
9group 'io.openliberty.deepdive'
10
11sourceCompatibility = 17
12targetCompatibility = 17
13tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
14 options.encoding = 'UTF-8'
15}
16
17repositories {
18 mavenCentral()
19}
20
21dependencies {
22 // provided dependencies
23 providedCompile 'jakarta.platform:jakarta.jakartaee-api:10.0.0'
24 providedCompile 'org.eclipse.microprofile:microprofile:6.1'
25}
26
27// tag::war[]
28war {
29 archiveVersion = ''
30}
31// end::war[]
32
33// tag::ext[]
34ext {
35 // tag::httpPort[]
36 liberty.server.var.'default.http.port' = '9080'
37 // end::httpPort[]
38 // tag::httpsPort[]
39 liberty.server.var.'default.https.port' = '9443'
40 // end::httpsPort[]
41 // tag::contextRoot[]
42 liberty.server.var.'default.context.root' = '/inventory'
43 // end::contextRoot[]
44}
45// end::ext[]
46
47clean.dependsOn 'libertyStop'When you are finished trying out changing this configuration, change the variables back to their original values.
-
update
liberty.var.http.portto9080 -
update
liberty.var.https.portto9443 -
update
liberty.var.context.rootto/inventory.
Replace thebuild.gradlefile.build.gradle
build.gradle
Injecting static configuration
You can now explore how to use MicroProfile’s Config API to inject static configuration into your microservice.
The MicroProfile Config API is included in the MicroProfile dependency that is specified in your build.gradle file. Look for the dependency with the microprofile artifact ID. This dependency provides a library that allows the use of the MicroProfile Config API. The microProfile feature is also enabled in the server.xml configuration file.
First, you need to edit the SystemResource class to inject static configuration into the CLIENT_PORT variable.
Replace theSystemResourceclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
The @Inject annotation injects the value from other configuration sources to the CLIENT_PORT variable. The @ConfigProperty defines the external property name as client.https.port.
Update the POST request so that the /client/{hostname} endpoint prints the CLIENT_PORT value.
Adding the microprofile-config.properties file
Define the configurable variables in the microprofile-config.properties configuration file for MicroProfile Config at the src/main/resources/META-INF directory.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
mkdir src\main\resources\META-INFmkdir -p src/main/resources/META-INFCreate themicroprofile-config.propertiesfile.src/main/resources/META-INF/microprofile-config.properties
microprofile-config.properties
Using the config_ordinal variable in this properties file, you can set the ordinal of this file and thus other configuration sources.
The client.https.port variable enables the client port to be overwritten.
Revisit the OpenAPI UI http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui to view these changes. Open the /api/systems/client/{hostname} endpoint and run it within the UI to view the CLIENT_PORT value.
You can learn more about MicroProfile Config from the Configuring microservices guide.
Persisting data
Next, you’ll persist the system data into the PostgreSQL database by using the Jakarta Persistence API (JPA).
Navigate to your application directory.
cd start/inventoryDefining a JPA entity class
To store Java objects in a database, you must define a JPA entity class. A JPA entity is a Java object whose nontransient and nonstatic fields are persisted to the database. Any POJO class can be designated as a JPA entity. However, the class must be annotated with the @Entity annotation, must not be declared final, and must have a public or protected nonargument constructor. JPA maps an entity type to a database table and persisted instances will be represented as rows in the table.
The SystemData class is a data model that represents systems in the inventory microservice. Annotate it with JPA annotations.
Replace theSystemDataclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/model/SystemData.java
SystemData.java
The following table breaks down the new annotations:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
|
Declares the class as an entity. |
|
Specifies details of the table such as name. |
|
Specifies a predefined database query that is run by an |
|
Declares the primary key of the entity. |
|
Specifies the strategy that is used for generating the value of the primary key. The |
|
Specifies that the field is mapped to a column in the database table. The |
Performing CRUD operations using JPA
The create, retrieve, update, and delete (CRUD) operations are defined in the Inventory. To perform these operations by using JPA, you need to update the Inventory class.
Replace theInventoryclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/Inventory.java
Inventory.java
To use the entity manager at run time, inject it into your CDI bean through the @PersistenceContext annotation. The entity manager interacts with the persistence context. Every EntityManager instance is associated with a persistence context. The persistence context manages a set of entities and is aware of the different states that an entity can have. The persistence context synchronizes with the database when a transaction commits.
SystemData.java
The Inventory class has a method for each CRUD operation, so let’s break them down:
-
The
add()method persists an instance of theSystemDataentity class to the data store by calling thepersist()method on anEntityManagerinstance. The entity instance becomes managed and changes to it are tracked by the entity manager. -
The
getSystems()method demonstrates a way to retrieve system objects from the database. This method returns a list of instances of theSystemDataentity class by using theSystemData.findAllquery that is specified in the@NamedQueryannotation on theSystemDataclass. Similarly, thegetSystem()method uses theSystemData.findSystemnamed query to find a system with the given hostname. -
The
update()method creates a managed instance of a detached entity instance. The entity manager automatically tracks all managed entity objects in its persistence context for changes and synchronizes them with the database. However, if an entity becomes detached, you must merge that entity into the persistence context by calling themerge()method so that changes to loaded fields of the detached entity are tracked. -
The
removeSystem()method removes an instance of theSystemDataentity class from the database by calling theremove()method on anEntityManagerinstance. The state of the entity is changed to removed and is removed from the database upon transaction commit.
Declare the endpoints with transaction management.
Replace theSystemResourceclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
The @Transactional annotation is used in the POST, PUT, and DELETE endpoints of the SystemResource class to declaratively control the transaction boundaries on the inventory CDI bean. This configuration ensures that the methods run within the boundaries of an active global transaction, and therefore you don’t need to explicitly begin, commit, or rollback transactions. At the end of the transactional method invocation, the transaction commits and the persistence context flushes any changes to the Event entity instances that it is managing to the database.
Configuring JPA
The persistence.xml file is a configuration file that defines a persistence unit. The
persistence unit specifies configuration information for the entity manager.
Create the configuration file.
src/main/resources/META-INF/persistence.xml
persistence.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<persistence version="2.2"
3 xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence"
4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence
6 http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_2.xsd">
7 <!-- tag::persistence-unit[] -->
8 <!-- tag::transaction-type[] -->
9 <persistence-unit name="jpa-unit" transaction-type="JTA">
10 <!-- end::transaction-type[] -->
11 <!-- tag::jta-data[] -->
12 <jta-data-source>jdbc/postgresql</jta-data-source>
13 <class>io.openliberty.deepdive.rest.model.SystemData</class>
14 <exclude-unlisted-classes>false</exclude-unlisted-classes>
15 <properties>
16 <property name="jakarta.persistence.schema-generation.database.action"
17 value="create"/>
18 <property name="jakarta.persistence.schema-generation.scripts.action"
19 value="create"/>
20 <property name="jakarta.persistence.schema-generation.scripts.create-target"
21 value="createDDL.ddl"/>
22 </properties>
23 </persistence-unit>
24 <!-- end::persistence-unit[] -->
25</persistence>The persistence unit is defined by the persistence-unit XML element. The name attribute is required. This attribute identifies the persistent unit when you use the @PersistenceContext annotation to inject the entity manager later in this exercise. The transaction-type="JTA" attribute specifies to use Java Transaction API (JTA) transaction management. When you use a container-managed entity manager, you must use JTA transactions.
A JTA transaction type requires a JTA data source to be provided. The jta-data-source element specifies the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) name of the data source that is used.
Configure the jdbc/postgresql data source in the Liberty server.xml configuration file.
Replace the Libertyserver.xmlconfiguration file.src/main/liberty/config/server.xml
server.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<server description="inventory">
3
4 <featureManager>
5 <feature>jakartaee-10.0</feature>
6 <feature>microProfile-6.0</feature>
7 </featureManager>
8
9 <variable name="default.http.port" defaultValue="9080" />
10 <variable name="default.https.port" defaultValue="9443" />
11 <variable name="default.context.root" defaultValue="/inventory" />
12 <variable name="postgres/hostname" defaultValue="localhost" />
13 <variable name="postgres/portnum" defaultValue="5432" />
14
15 <httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint" host="*"
16 httpPort="${default.http.port}"
17 httpsPort="${default.https.port}" />
18
19 <!-- Automatically expand WAR files and EAR files -->
20 <applicationManager autoExpand="true"/>
21
22 <!-- Configures the application on a specified context root -->
23 <webApplication contextRoot="${default.context.root}"
24 location="inventory.war" />
25
26 <!-- Default SSL configuration enables trust for default certificates from the Java runtime -->
27 <ssl id="defaultSSLConfig" trustDefaultCerts="true" />
28
29 <!-- tag::postgresqlLibrary[] -->
30 <library id="postgresql-library">
31 <fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/" includes="*.jar" />
32 </library>
33 <!-- end::postgresqlLibrary[] -->
34
35 <!-- Datasource Configuration -->
36 <!-- tag::dataSource[] -->
37 <dataSource id="DefaultDataSource" jndiName="jdbc/postgresql">
38 <jdbcDriver libraryRef="postgresql-library" />
39 <properties.postgresql databaseName="admin"
40 serverName="localhost"
41 portNumber="5432"
42 user="admin"
43 password="adminpwd"/>
44 </dataSource>
45 <!-- end::dataSource[] -->
46</server>The library element tells the Liberty where to find the PostgreSQL library. The dataSource element points to where the Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) driver connects, along with some database vendor-specific properties. For more information, see the Data source configuration and dataSource element documentation.
To use a PostgreSQL database, you need to download its library and store it to the Liberty shared resources directory. Configure the Liberty Maven plug-in in the build.gradle file.
Replace thebuild.gradleconfiguration file.build.gradle
build.gradle
The postgresql dependency under the jdbcLib configuration ensures that Gradle downloads the PostgreSQL library to local project. The copyJdbcLibs task copies the library to the Liberty shared resources directory and ensures that the driver is available for the Liberty server’s use each time the project is built. To make the persistence.xml file available in the Liberty loose application configuration, set the value for the Gradle resourcesDir output directory location to be the Gradle destinationDirectory directory. The Gradle project generates the resources artifacts into the resourcesDir directory and the Java class files into the destinationDirectory directory.
Starting PostgreSQL database
Use Docker to run an instance of the PostgreSQL database for a fast installation and setup.
A container file is provided for you. First, navigate to the finish/postgres directory. Then, run the following commands to use the Dockerfile to build the image, run the image in a Docker container, and map 5432 port from the container to your machine:
cd ../../finish/postgres
podman build -t postgres-sample .
podman run --name postgres-container -p 5432:5432 -d postgres-sampleRunning the application
In your dev mode console for the inventory microservice, type r and press enter/return key to restart the Liberty instance.
After you see the following message, your Liberty instance is ready in dev mode again:
************************************************************** * Liberty is running in dev mode.
Point your browser to the http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui URL. This URL displays the available REST endpoints.
First, make a POST request to the /api/systems/ endpoint. To make this request, expand the first POST endpoint on the UI, click the Try it out button, provide values to the heapSize, hostname, javaVersion, and osName parameters, and then click the Execute button. The POST request adds a system with the specified values to the database.
Next, make a GET request to the /api/systems endpoint. To make this request, expand the GET endpoint on the UI, click the Try it out button, and then click the Execute button. The GET request returns all systems from the database.
Next, make a PUT request to the /api/systems/{hostname} endpoint. To make this request, expand the PUT endpoint on the UI, click the Try it out button. Then, provide the same value to the hostname parameter as in the previous step, provide different values to the heapSize, javaVersion, and osName parameters, and click the Execute button. The PUT request updates the system with the specified values.
To see the updated system, make a GET request to the /api/systems/{hostname} endpoint. To make this request, expand the GET endpoint on the UI, click the Try it out button, provide the same value to the hostname parameter as the previous step, and then click the Execute button. The GET request returns the system from the database.
Next, make a DELETE request to the /api/systems/{hostname} endpoint. To make this request, expand the DELETE endpoint on the UI, click the Try it out button, and then click Execute. The DELETE request removes the system from the database. Run the GET request again to see that the system no longer exists in the database.
Securing RESTful APIs
Now you can secure your RESTful APIs. Navigate to your application directory.
cd start/inventoryBegin by adding some users and user groups to your Liberty server.xml configuration file.
Replace the Libertyserver.xmlconfiguration file.src/main/liberty/config/server.xml
server.xml
The basicRegistry element contains a list of all users for the application and their passwords, as well as all of the user groups. Note that this basicRegistry element is a very simple case for learning purposes. For more information about the different user registries, see the User registries documentation. The admin group tells the application which of the users are in the administrator group. The user group tells the application that users are in the user group.
The security-role maps the admin role to the admin group, meaning that all users in the admin group have the administrator role. Similarly, the user role is mapped to the user group, meaning all users in the user group have the user role.
Your application has the following users and passwords:
Username |
Password |
Role |
bob |
bobpwd |
admin, user |
alice |
alicepwd |
user |
Now you can secure the inventory service.
Replace theSystemResourceclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
This class now has role-based access control. The role names that are used in the @RolesAllowed annotations are mapped to group names in the groups claim of the JSON Web Token (JWT). This mapping results in an authorization decision wherever the security constraint is applied.
The /{hostname} endpoint that is annotated with the @PUT annotation updates a system in the inventory. This PUT endpoint is annotated with the @RolesAllowed({ "admin", "user" }) annotation. Only authenticated users with the role of admin or user can access this endpoint.
The /{hostname} endpoint that is annotated with the @DELETE annotation removes a system from the inventory. This DELETE endpoint is annotated with the @RolesAllowed({ "admin" }) annotation. Only authenticated users with the role of admin can access this endpoint.
You can manually check that the inventory microservice is secured by making requests to the PUT and DELETE endpoints.
Before making requests, you must add a system to the inventory. Try adding a system by using the POST endpoint /systems by running the following command:
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:9080/inventory/api/systems?hostname=localhost&osName=mac&javaVersion=17&heapSize=1'
You can expect the following response:
{ "ok" : "localhost was added." }This command calls the /systems endpoint and adds a system localhost to the inventory. You can validate that the command worked by calling the /systems endpoint with a GET request to retrieve all the systems in the inventory, with the following curl command:
curl -s 'http://localhost:9080/inventory/api/systems'
You can now expect the following response:
[{"heapSize":1,"hostname":"localhost","javaVersion":"17","osName":"mac","id":23}]Now try calling your secure PUT endpoint to update the system that you just added by the following curl command:
curl -k --user alice:alicepwd -X PUT 'http://localhost:9080/inventory/api/systems/localhost?heapSize=2097152&javaVersion=17&osName=linux'
As this endpoint is accessible to the groups user and admin, you must log in with user credentials to update the system.
You should see the following response:
{ "ok" : "localhost was updated." }This response means that you logged in successfully as an authenticated user, and that the endpoint works as expected.
Now try calling the DELETE endpoint. As this endpoint is only accessible to admin users, you can expect this command to fail if you attempt to access it with a user in the user group.
You can check that your application is secured against these requests with the following command:
curl -kf --user alice:alicepwd -X DELETE 'https://localhost:9443/inventory/api/systems/localhost'
You should see the following response:
curl: (22) The requested URL returned error: 403As alice is part of the user group, this request cannot work. In your dev mode console, you can expect the following output:
jakarta.ws.rs.ForbiddenException: UnauthorizedNow attempt to call this endpoint with an authenticated admin user that can work correctly. Run the following curl command:
curl -k --user bob:bobpwd -X DELETE 'https://localhost:9443/inventory/api/systems/localhost'
You can expect to see the following response:
{ "ok" : "localhost was removed." }This response means that your endpoint is secure. Validate that it works correctly by calling the /systems endpoint with the following curl command:
curl 'http://localhost:9080/inventory/api/systems'
You can expect to see the following output:
[]This response shows that the endpoints work as expected and that the system you added was successfully deleted.
Consuming the secured RESTful APIs by JWT
You can now implement JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and configure them as Single Sign On (SSO) cookies to use the RESTful APIs. The JWT that is generated by Liberty is used to communicate securely between the inventory and system microservices. You can implement the /client/{hostname} POST endpoint to collect the properties from the system microservices and create a system in the inventory.
The system microservice is provided for you.
Writing the RESTful client interface
Create the client subdirectory. Then, create a RESTful client interface for the system microservice in the inventory microservice.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
mkdir src\main\java\io\openliberty\deepdive\rest\clientmkdir src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/clientCreate theSystemClientinterface.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/client/SystemClient.java
SystemClient.java
This interface declares methods for accessing each of the endpoints that are set up for you in the system service. The MicroProfile Rest Client feature automatically builds and generates a client implementation based on what is defined in the SystemClient interface. You don’t need to set up the client and connect with the remote service.
Now create the required exception classes that are used by the SystemClient instance.
Create theUnknownUriExceptionclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/client/UnknownUriException.java
UnknownUriException.java
This class is an exception that is thrown when an unknown URI is passed to the SystemClient.
Create theUnknownUriExceptionMapperclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/client/UnknownUriExceptionMapper.java
UnknownUriExceptionMapper.java
This class links the UnknownUriException class with the corresponding response code through a ResponseExceptionMapper mapper class.
Implementing the /client/{hostname} endpoint
Now implement the /client/{hostname} POST endpoint of the SystemResource class to consume the secured system microservice.
Replace theSystemResourceclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
The getSystemClient() method builds and returns a new instance of the SystemClient class for the hostname provided. The /client/{hostname} POST endpoint uses this method to create a REST client that is called customRestClient to consume the system microservice.
A JWT instance is injected to the jwt field variable by the jwtSso feature. It is used to create the authHeader authentication header. It is then passed as a parameter to the endpoints of the customRestClient to get the properties from the system microservice. A system is then added to the inventory.
Configuring the JSON Web Token
Next, add the JSON Web Token (Single Sign On) feature to the Liberty server.xml configuration file for the inventory service.
Replace the Libertyserver.xmlconfiguration file.src/main/liberty/config/server.xml
server.xml
microprofile-config.properties
The jwtSso feature adds the libraries that are required for JWT SSO implementation. Configure the jwtSso feature by adding the jwtBuilder configuration to your server.xml file. Also, configure the MicroProfile JWT with the audiences and issuer properties that match the microprofile-config.properties defined at the system/src/main/webapp/META-INF directory under the system project. For more information, see the JSON Web Token Single Sign-On feature, jwtSso element, and jwtBuilder element documentation.
The keyStore element is used to define the repository of security certificates used for SSL encryption. The id attribute is a unique configuration ID that is set to guideKeyStore. The password attribute is used to load the keystore file, and its value can be stored in clear text or encoded form. To learn more about other attributes, see the keyStore attribute documentation.
To avoid the conflict with the default ssl configuration, define your own ssl configuration by setting the id attribute to other value, the sslDefault element, and the sslRef attribute in the mpJwt element.
Because the keystore file is not provided at the src directory, Liberty creates a Public Key Cryptography Standards #12 (PKCS12) keystore file for you by default. This file needs to be replaced, as the keyStore configuration must be the same in both system and inventory microservices. As the configured system microservice is already provided for you, copy the key.p12 keystore file from the system microservice to your inventory service.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
mkdir src\main\liberty\config\resources\security
copy ..\..\finish\system\src\main\liberty\config\resources\security\key.p12 src\main\liberty\config\resources\security\key.p12mkdir -p src/main/liberty/config/resources/security
cp ../../finish/system/src/main/liberty/config/resources/security/key.p12 src/main/liberty/config/resources/security/key.p12Now configure the client https port in the build.gradle configuration file.
Replace thebuild.gradlefile.build.gradle
build.gradle
Configure the client https port by setting the <liberty.var.client.https.port> to 9444.
In your dev mode console for the inventory microservice, press CTRL+C to stop the Liberty instance. Then, restart the dev mode of the inventory microservice.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
gradlew libertyDev./gradlew libertyDevAfter you see the following message, your Liberty instance is ready in dev mode again:
************************************************************** * Liberty is running in dev mode.
Running the /client/{hostname} endpoint
Open another command-line session and run the system microservice from the finish directory.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
cd finish\system
gradlew libertyRuncd finish/system
./gradlew libertyRunWait until the following message displays on the system microservice console.
CWWKF0011I: The defaultServer server is ready to run a smarter planet. ...You can check that the system microservice is secured against unauthenticated requests at the https://localhost:9444/system/api/heapsize URL. Open another command-line session and run the following command:
curl -kf 'https://localhost:9444/system/api/heapsize'
You should see the following response:
curl: (22) The requested URL returned error: 401You can expect to see the following error in the console of the system microservice:
CWWKS5522E: The MicroProfile JWT feature cannot perform authentication because a MicroProfile JWT cannot be found in the request.You can check that the /client/{hostname} endpoint you updated can access the system microservice.
Make an authorized request to the new /client/{hostname} endpoint.
As this endpoint is restricted to admin, you can use the login credentials for bob, which is in the admin group.
curl -k --user bob:bobpwd -X POST 'https://localhost:9443/inventory/api/systems/client/localhost'
You can expect the following output:
{ "ok" : "localhost was added." }You can verify that this endpoint works as expected by running the following command:
curl 'http://localhost:9080/inventory/api/systems'
You can expect to see your system listed in the output.
[
{
"heapSize": 2999975936,
"hostname": "localhost",
"id": 11,
"javaVersion": "17.0.9",
"osName": "Linux"
}
]Adding health checks
Next, you’ll use MicroProfile Health to report the health status of the microservice and PostgreSQL database connection.
Navigate to your application directory
cd start/inventoryA health report is generated automatically for all health services that enable MicroProfile Health.
All health services must provide an implementation of the HealthCheck interface, which is used to verify their health. MicroProfile Health offers health checks for startup, liveness, and readiness.
A startup check allows applications to define startup probes that are used for initial verification of the application before the liveness probe takes over. For example, a startup check might check which applications require additional startup time on their first initialization.
A liveness check allows third-party services to determine whether a microservice is running. If the liveness check fails, the application can be terminated. For example, a liveness check might fail if the application runs out of memory.
A readiness check allows third-party services, such as Kubernetes, to determine whether a microservice is ready to process requests.
Create the health subdirectory before creating the health check classes.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
mkdir src\main\java\io\openliberty\deepdive\rest\healthmkdir src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/healthCreate theStartupCheckclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/health/StartupCheck.java
StartupCheck.java
The @Startup annotation indicates that this class is a startup health check procedure. Navigate to the http://localhost:9080/health/started URL to check the status of the startup health check. In this case, you are checking the cpu usage. If more than 95% of the cpu is being used, a status of DOWN is returned.
Create theLivenessCheckclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/health/LivenessCheck.java
LivenessCheck.java
The @Liveness annotation indicates that this class is a liveness health check procedure. Navigate to the http://localhost:9080/health/live URL to check the status of the liveness health check. In this case, you are checking the heap memory usage. If more than 90% of the maximum memory is being used, a status of DOWN is returned.
Create theReadinessCheckclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/health/ReadinessCheck.java
ReadinessCheck.java
The @Readiness annotation indicates that this class is a readiness health check procedure. Navigate to the http://localhost:9080/health/ready URL to check the status of the readiness health check. This readiness check tests the connection to the PostgreSQL container that was created earlier in the guide. If the connection is refused, a status of DOWN is returned.
Or, you can visit the http://localhost:9080/health URL to see the overall health status of the application.
Providing metrics
Next, you can learn how to use MicroProfile Metrics to provide metrics from the inventory microservice.
Go to your application directory.
cd start/inventoryEnable the bob user to access the /metrics endpoints.
Replace the Libertyserver.xmlconfiguration file.src/main/liberty/config/server.xml
server.xml
The administrator-role configuration authorizes the bob user as an administrator.
Use annotations that are provided by MicroProfile Metrics to instrument the inventory microservice to provide application-level metrics data.
Replace theSystemResourceclass.src/main/java/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResource.java
SystemResource.java
Import the Counted annotation and apply it to the POST /api/systems, PUT /api/systems/{hostname}, DELETE /api/systems/{hostname}, and POST /api/systems/client/{hostname} endpoints to monotonically count how many times that the endpoints are accessed.
Additional information about the annotations that MicroProfile metrics provides, relevant metadata fields, and more are available at the MicroProfile Metrics Annotation Javadoc.
Point your browser to the http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui URL to try out your application and call some of the endpoints that you annotated.
MicroProfile Metrics provides 4 different REST endpoints.
-
The
/metricsendpoint provides you with all the metrics in text format. -
The
/metrics?scope=applicationendpoint provides you with application-specific metrics. -
The
/metrics?scope=baseendpoint provides you with metrics that are defined in MicroProfile specifications. Metrics in the base scope are intended to be portable between different MicroProfile-compatible runtimes. -
The
/metrics?scope=vendorendpoint provides you with metrics that are specific to the runtime.
Point your browser to the https://localhost:9443/metrics URL to review all the metrics that are enabled through MicroProfile Metrics. Log in with bob as your username and bobpwd as your password. You can see the metrics in text format.
To see only the application metrics, point your browser to https://localhost:9443/metrics?scope=application. You can expect to see your application metrics in the output.
# HELP updateSystem_total Number of times updating a system endpoint is called
# TYPE updateSystem_total counter
updateSystem_total{mp_scope="application",} 1.0
# HELP removeSystem_total Number of times removing a system endpoint is called
# TYPE removeSystem_total counter
removeSystem_total{mp_scope="application",} 1.0
# HELP addSystemClient_total Number of times adding a system by client is called
# TYPE addSystemClient_total counter
addSystemClient_total{mp_scope="application",} 0.0
# HELP addSystem_total Number of times adding system endpoint is called
# TYPE addSystem_total counter
addSystem_total{mp_scope="application",} 1.0You can see the system metrics at the https://localhost:9443/metrics?scope=base URL. You can also see the vendor metrics at the https://localhost:9443/metrics?scope=vendor URL.
Building the container
Press CTRL+C in the command-line session to stop the gradlew libertyDev dev mode that you started in the previous section.
Navigate to your application directory:
cd start/inventoryThe first step to containerizing your application inside of a container is creating a Containerfile. A Containerfile is a collection of instructions for building a container image that can then be run as a container.
Make sure to start your podman daemon before you proceed.
Create theContainerfilein thestart/inventorydirectory.Containerfile
Containerfile
1# tag::from[]
2FROM icr.io/appcafe/open-liberty:full-java11-openj9-ubi
3# end::from[]
4
5ARG VERSION=1.0
6ARG REVISION=SNAPSHOT
7
8# tag::label[]
9LABEL \
10 org.opencontainers.image.authors="My Name" \
11 org.opencontainers.image.vendor="Open Liberty" \
12 org.opencontainers.image.url="local" \
13 org.opencontainers.image.source="https://github.com/OpenLiberty/guide-liberty-deepdive-gradle" \
14 org.opencontainers.image.version="$VERSION" \
15 org.opencontainers.image.revision="$REVISION" \
16 vendor="Open Liberty" \
17 name="inventory" \
18 version="$VERSION-$REVISION" \
19 summary="" \
20 description="This image contains the inventory microservice running with the Open Liberty runtime."
21# end::label[]
22
23USER root
24
25# tag::copy[]
26# tag::copy-config[]
27# tag::config-userID[]
28COPY --chown=1001:0 \
29# end::config-userID[]
30 # tag::inventory-config[]
31 src/main/liberty/config/ \
32 # end::inventory-config[]
33 # tag::config[]
34 /config/
35 # end::config[]
36# end::copy-config[]
37
38# tag::copy-war[]
39# tag::war-userID[]
40COPY --chown=1001:0 \
41# end::war-userID[]
42 # tag::inventory-war[]
43 build/libs/inventory.war \
44 # end::inventory-war[]
45 # tag::config-apps[]
46 /config/apps
47 # end::config-apps[]
48# end::copy-war[]
49
50# tag::copy-jar[]
51# tag::jar-userID[]
52COPY --chown=1001:0 \
53# end::jar-userID[]
54 # tag::inventory-jar[]
55 build/wlp/usr/shared/resources/*.jar \
56 # end::inventory-jar[]
57 # tag::shared-resources[]
58 /opt/ol/wlp/usr/shared/resources/
59 # end::shared-resources[]
60# end::copy-jar[]
61# end::copy[]
62
63USER 1001
64
65RUN configure.shThe FROM instruction initializes a new build stage and indicates the parent image from which your image is built. In this case, you’re using the icr.io/appcafe/open-liberty:full-java17-openj9-ubi image that comes with the latest Open Liberty runtime as your parent image.
To help you manage your images, you can label your container images with the LABEL command.
The COPY instructions are structured as COPY [--chown=<user>:<group>] <source> <destination>. They copy local files into the specified destination within your container image. In this case, the first COPY instruction copies the Liberty configuration file that is at src/main/liberty/config/server.xml to the /config/ destination directory. Similarly, the second COPY instruction copies the .war file to the /config/apps destination directory. The third COPY instruction copies the PostgreSQL library file to the Liberty shared resources directory.
Developing the application in a container
Make the PostgreSQL database configurable in the Liberty server.xml configuraton file.
Replace the Libertyserver.xmlconfiguration file.src/main/liberty/config/server.xml
server.xml
Instead of the hard-coded serverName, portNumber, user, and password values in the properties.postgresql properties, use ${postgres/hostname}, ${postgres/portnum}, ${postgres/username}, and ${postgres/password}, which are defined by the variable elements.
You can use the Containerfile to try out your application with the PostGreSQL database by running the devc goal.
The Open Liberty Maven plug-in includes a devc goal that simplifies developing your application in a container by starting dev mode with container support. This goal builds a Podman image, mounts the required directories, binds the required ports, and then runs the application inside of a container. Dev mode also listens for any changes in the application source code or configuration and rebuilds the image and restarts the container as necessary.
Retrieve the PostgreSQL container IP address by running the following command:
podman inspect -f "{{.NetworkSettings.IPAddress }}" postgres-containerThe command returns the PostgreSQL container IP address:
172.17.0.2
Build and run the container by running the devc goal with the PostgreSQL container IP address from the start/inventory directory. If your PostgreSQL container IP address is not 172.17.0.2, replace the command with the right IP address.
mvn liberty:devc -DdockerRunOpts="-e POSTGRES_HOSTNAME=172.17.0.2" -DserverStartTimeout=240You need to wait a while to let dev mode start. After you see the following message, your Liberty instance is ready in dev mode:
************************************************************** * Liberty is running in dev mode. * ... * Podman network information: * Container name: [ liberty-dev ] * IP address [ 172.17.0.2 ] on Docker network [ bridge ] * ...
Open another command-line session and run the following command to make sure that your container is running and didn’t crash:
podman psYou can see something similar to the following output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES ee2daf0b33e1 inventory-dev-mode "/opt/ol/helpers/run…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:7777->7777/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9080->9080/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9443->9443/tcp liberty-dev
Point your browser to the http://localhost:9080/openapi/ui URL to try out your application.
When you’re finished trying out the microservice, press CTRL+C in the command-line session where you started dev mode to stop and remove the container.
Also, run the following commands to stop the PostgreSQL container that was started in the previous section.
podman stop postgres-container
podman rm postgres-containerBuilding the container image
Run the war task from the start/inventory directory so that the .war file resides in the build/libs directory.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
gradlew war./gradlew warBuild your container image with the following commands:
podman build -t liberty-deepdive-inventory:1.0-SNAPSHOT .When the build finishes, run the following command to list all local container images:
podman imagesVerify that the liberty-deepdive-inventory:1.0-SNAPSHOT image is listed among the container images, for example:
REPOSITORY TAG
liberty-deepdive-inventory 1.0-SNAPSHOT
icr.io/appcafe/open-liberty full-java17-openj9-ubiTesting the microservice with Testcontainers
Although you can test your microservice manually, you should rely on automated tests. In this section, you can learn how to use Testcontainers to verify your microservice in the same Docker container that you’ll use in production.
First, create the test directory at the src directory of your Gradle project.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
mkdir src\test\java\it\io\openliberty\deepdive\rest
mkdir src\test\resourcesmkdir -p src/test/java/it/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest
mkdir src/test/resourcesCreate a RESTful client interface for the inventory microservice.
Create theSystemResourceClient.javafile.src/test/java/it/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResourceClient.java
SystemResourceClient.java
This interface declares listContents(), getSystem(), addSystem(), updateSystem(), and removeSystem() methods for accessing each of the endpoints that are set up to access the inventory microservice.
Create the SystemData data model for each system in the inventory.
Create theSystemData.javafile.src/test/java/it/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemData.java
SystemData.java
The SystemData class contains the ID, hostname, operating system name, Java version, and heap size properties. The various get and set methods within this class enable you to view and edit the properties of each system in the inventory.
Create the test container class that access the inventory docker image that you built in previous section.
Create theLibertyContainer.javafile.src/test/java/it/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/LibertyContainer.java
LibertyContainer.java
The createRestClient() method creates a REST client instance with the SystemResourceClient interface. The getBaseURL() method constructs the URL that can access the inventory docker image.
Now, you can create your integration test cases.
Create theSystemResourceIT.javafile.src/test/java/it/io/openliberty/deepdive/rest/SystemResourceIT.java
SystemResourceIT.java
Define the postgresContainer test container to start up the PostgreSQL docker image, and define the libertyContainer test container to start up the inventory docker image. Make sure that both containers use the same network. The /health/ready endpoint can tell you whether the container is ready to start testing.
The testAddSystem() verifies the addSystem and listContents endpoints.
The testUpdateSystem() verifies the updateSystem and getSystem endpoints.
The testRemoveSystem() verifies the removeSystem endpoint.
Create the log4j properites that are required by the Testcontainers framework.
Create thelog4j.propertiesfile.src/test/resources/log4j.properties
log4j.properties
Update the Gradle configuration file with the required dependencies.
Replace thebuild.gradlefile.build.gradle
build.gradle
Add each required dependency with test scope, including JUnit5, Testcontainers, Log4J, JBoss RESTEasy client, Glassfish JSON, and Vert.x libraries. Also, add the io.openliberty.tools.gradle.Liberty plugin, so that the integration test can be run by the Gradle verify goal.
Running the tests
You can run the Gradle verify goal, which compiles the java files, starts the containers, runs the tests, and then stops the containers.
WINDOWS
MAC
LINUX
gradlew verify.\gradlew verifyexport TESTCONTAINERS_RYUK_DISABLED=true
mvn verifyYou will see the following output:
-------------------------------------------------------
T E S T S
-------------------------------------------------------
Running it.io.openliberty.deepdive.rest.SystemResourceIT
...
Tests run: 3, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0, Time elapsed: 17.413 s - in it.io.openliberty.deepdive.rest.SystemResourceIT
Results :
Tests run: 3, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Skipped: 0Starting and preparing your cluster for deployment
If you are using Linux, you can continue this section.
Start your Kubernetes cluster.
Run the following command from a command-line session:
minikube startNext, validate that you have a healthy Kubernetes environment by running the following command from the active command-line session.
kubectl get nodesThis command should return a Ready status for the minikube node.
Run the following command to configure the Docker CLI to use Minikube’s Docker daemon. After you run this command, you will be able to interact with Minikube’s Docker daemon and build new images directly to it from your host machine:
eval $(minikube docker-env)Rebuild your Docker image under Minikube with the following commands:
docker build -t liberty-deepdive-inventory:1.0-SNAPSHOT .Deploying the microservice to Kubernetes
If you are using Linux, you can continue this section.
Now that the containerized application is built and tested, deploy it to a local Kubernetes cluster.
Installing the Open Liberty Operator
Install the Open Liberty Operator to deploy the microservice to Kubernetes.
First, install the cert-manager to your Kubernetes cluster by running the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.12.3/cert-manager.yamlNext, install Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) for the Open Liberty Operator by running the following command:
kubectl apply --server-side -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenLiberty/open-liberty-operator/main/deploy/releases/1.2.1/kubectl/openliberty-app-crd.yamlCustom Resources extend the Kubernetes API and enhance its functionality.
Set environment variables for namespaces for the Open Liberty Operator by running the following commands:
OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=default
WATCH_NAMESPACE='""'Next, run the following commands to install cluster-level role-based access:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenLiberty/open-liberty-operator/main/deploy/releases/1.2.1/kubectl/openliberty-app-rbac-watch-all.yaml \
| sed -e "s/OPEN_LIBERTY_OPERATOR_NAMESPACE/${OPERATOR_NAMESPACE}/" \
| kubectl apply -f -Finally, run the following commands to install the Operator:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenLiberty/open-liberty-operator/main/deploy/releases/1.2.1/kubectl/openliberty-app-operator.yaml \
| sed -e "s/OPEN_LIBERTY_WATCH_NAMESPACE/${WATCH_NAMESPACE}/" \
| kubectl apply -n ${OPERATOR_NAMESPACE} -f -To check that the Open Liberty Operator is installed successfully, run the following command to view all the supported API resources that are available through the Open Liberty Operator:
kubectl api-resources --api-group=apps.openliberty.ioLook for the following output, which shows the custom resource definitions (CRDs) that can be used by the Open Liberty Operator:
NAME SHORTNAMES APIGROUP NAMESPACED KIND
openlibertyapplications olapp,olapps apps.openliberty.io true OpenLibertyApplication
openlibertydumps oldump,oldumps apps.openliberty.io true OpenLibertyDump
openlibertytraces oltrace,oltraces apps.openliberty.io true OpenLibertyTraceEach CRD defines a kind of object that can be used, which is specified in the previous example by the KIND value. The SHORTNAME value specifies alternative names that you can substitute in the configuration to refer to an object kind. For example, you can refer to the OpenLibertyApplication object kind by one of its specified shortnames, such as olapps.
The openlibertyapplications CRD defines a set of configurations for deploying an Open Liberty-based application, including the application image, number of instances, and storage settings. The Open Liberty Operator watches for changes to instances of the OpenLibertyApplication object kind and creates Kubernetes resources that are based on the configuration that is defined in the CRD.
Deploying the container image
Create theinventory.yamlin thestart/inventorydirectory.inventory.yaml
inventory.yaml
1apiVersion: apps.openliberty.io/v1beta2
2# tag::kind[]
3kind: OpenLibertyApplication
4# end::kind[]
5metadata:
6 name: inventory-deployment
7 labels:
8 name: inventory-deployment
9spec:
10 # tag::applicationImage[]
11 applicationImage: liberty-deepdive-inventory:1.0-SNAPSHOT
12 # end::applicationImage[]
13 service:
14 port: 9443
15 env:
16 - name: POSTGRES_HOSTNAME
17 value: "postgres"In the inventory.yaml file, the custom resource (CR) is specified to be OpenLibertyApplication. The CR triggers the Open Liberty Operator to create, update, or delete Kubernetes resources that are needed by the application to run on your cluster. Additionally, the applicationImage field must be specified and set to the image that was created in the previous module.
postgres.yaml
1kind: ConfigMap
2apiVersion: v1
3metadata:
4 namespace: default
5 name: poststarthook
6data:
7 schema.sql: |
8 CREATE TABLE SystemData (
9 id SERIAL,
10 hostname varchar(50),
11 osName varchar(50),
12 javaVersion varchar(50),
13 heapSize bigint,
14 primary key(id)
15 );
16
17 CREATE SEQUENCE systemData_id
18 START 1
19 INCREMENT 1
20 OWNED BY SystemData.id;
21---
22# tag::deployment[]
23apiVersion: apps/v1
24kind: Deployment
25metadata:
26 name: postgres
27 labels:
28 app: postgres
29 group: db
30spec:
31 replicas: 1
32 selector:
33 matchLabels:
34 app: postgres
35 template:
36 metadata:
37 labels:
38 app: postgres
39 type: db
40 spec:
41 volumes:
42 - name: hookvolume
43 configMap:
44 name: poststarthook
45 defaultMode: 0755
46 containers:
47 - name: postgres
48 image: postgres:14.1
49 ports:
50 - containerPort: 5432
51 volumeMounts:
52 - name: hookvolume
53 mountPath: /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d
54 # tag::env[]
55 env:
56 - name: POSTGRES_USER
57 valueFrom:
58 secretKeyRef:
59 name: post-app-credentials
60 key: username
61 - name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD
62 valueFrom:
63 secretKeyRef:
64 name: post-app-credentials
65 key: password
66 # end::env[]
67# end::deployment[]
68---
69# tag::service[]
70apiVersion: v1
71kind: Service
72metadata:
73 name: postgres
74 labels:
75 group: db
76spec:
77 type: ClusterIP
78 selector:
79 app: postgres
80 ports:
81 - protocol: TCP
82 port: 5432
83# tag::service[]Similarly, a Kubernetes resource definition is provided in the postgres.yaml file at the finish/postgres directory. In the postgres.yaml file, the deployment for the PostgreSQL database is defined.
Create a Kubernetes Secret to configure the credentials for the admin user to access the database.
kubectl create secret generic post-app-credentials --from-literal username=admin --from-literal password=adminpwdThe credentials are passed to the PostgreSQL database service as environment variables in the env field.
Run the following command to deploy the application and database:
kubectl apply -f ../../finish/postgres/postgres.yaml
kubectl apply -f inventory.yamlWhen your pods are deployed, run the following command to check their status:
kubectl get podsIf all the pods are working correctly, you see an output similar to the following example:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE inventory-deployment-75f9dc56d9-g9lzl 1/1 Running 0 35s postgres-58bd9b55c7-6vzz8 1/1 Running 0 13s olo-controller-manager-6fc6b456dc-s29wl 1/1 Running 0 10m
Pause briefly to give the inventory service time to initialize. After it has started, use the following command to configure port forwarding to access the inventory microservice:
kubectl port-forward svc/inventory-deployment 9443The port-forward command pauses the command-line session until you press Ctrl+C after you try out the microservice.
The application might take some time to get ready. See the https://localhost:9443/health URL to confirm that the inventory microservice is up and running.
Once your application is up and running, you can check out the service at the https://localhost:9443/openapi/ui/ URL. The servers dropdown list shows the https://localhost:9443/inventory URL. Or, you can run the following command to access the inventory microservice:
curl -k https://localhost:9443/inventory/api/systemsWhen you’re done trying out the microservice, press CTRL+C in the command line session where you ran the kubectl port-forward command to stop the port forwarding. Then, run the kubectl delete command to stop the inventory microservice.
kubectl delete -f inventory.yamlCustomizing deployments
server.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<server description="inventory">
3
4 <featureManager>
5 <feature>jakartaee-10.0</feature>
6 <feature>microProfile-6.0</feature>
7 <feature>jwtSso-1.0</feature>
8 </featureManager>
9
10 <variable name="default.http.port" defaultValue="9080" />
11 <variable name="default.https.port" defaultValue="9443" />
12 <!-- tag::contextRoot[] -->
13 <variable name="default.context.root" defaultValue="/inventory" />
14 <!-- end::contextRoot[] -->
15 <!-- tag::variables[] -->
16 <variable name="postgres/hostname" defaultValue="localhost" />
17 <variable name="postgres/portnum" defaultValue="5432" />
18 <variable name="postgres/username" defaultValue="admin" />
19 <variable name="postgres/password" defaultValue="adminpwd" />
20 <!-- end::variables[] -->
21
22 <httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint" host="*"
23 httpPort="${default.http.port}"
24 httpsPort="${default.https.port}" />
25
26 <!-- Automatically expand WAR files and EAR files -->
27 <applicationManager autoExpand="true"/>
28
29 <keyStore id="defaultKeyStore" password="secret" />
30
31 <basicRegistry id="basic" realm="WebRealm">
32 <user name="bob" password="{xor}PTA9Lyg7" />
33 <user name="alice" password="{xor}PjM2PDovKDs=" />
34
35 <group name="admin">
36 <member name="bob" />
37 </group>
38
39 <group name="user">
40 <member name="bob" />
41 <member name="alice" />
42 </group>
43 </basicRegistry>
44
45 <!-- Configures the application on a specified context root -->
46 <webApplication contextRoot="${default.context.root}"
47 location="inventory.war">
48 <application-bnd>
49 <security-role name="admin">
50 <group name="admin" />
51 </security-role>
52 <security-role name="user">
53 <group name="user" />
54 </security-role>
55 </application-bnd>
56 </webApplication>
57
58 <jwtSso jwtBuilderRef="jwtInventoryBuilder"/>
59 <jwtBuilder id="jwtInventoryBuilder"
60 issuer="http://openliberty.io"
61 audiences="systemService"
62 expiry="24h"/>
63 <mpJwt audiences="systemService"
64 groupNameAttribute="groups"
65 id="myMpJwt"
66 issuer="http://openliberty.io"/>
67
68 <!-- Default SSL configuration enables trust for default certificates from the Java runtime -->
69 <ssl id="defaultSSLConfig" trustDefaultCerts="true" />
70
71 <library id="postgresql-library">
72 <fileset dir="${shared.resource.dir}/" includes="*.jar" />
73 </library>
74
75 <dataSource id="DefaultDataSource" jndiName="jdbc/postgresql">
76 <jdbcDriver libraryRef="postgresql-library" />
77 <!-- tag::postgresProperties[] -->
78 <properties.postgresql databaseName="admin"
79 serverName="${postgres/hostname}"
80 portNumber="${postgres/portnum}"
81 user="${postgres/username}"
82 password="${postgres/password}"/>
83 <!-- end::postgresProperties[] -->
84 </dataSource>
85</server>You can modify the inventory deployment to customize the service. Customizations for a service include changing the port number, changing the context root, and passing confidential information by using Secrets.
The context.root variable is defined in the server.xml configuration file. The context root for the inventory service can be changed by using this variable. The value for the context.root variable can be defined in a ConfigMap and accessed as an environment variable.
Create a ConfigMap to configure the app name with the following kubectl command.
kubectl create configmap inv-app-root --from-literal contextRoot=/devThis command deploys a ConfigMap named inv-app-root to your cluster. It has a key called contextRoot with a value of /dev. The --from-literal flag specifies individual key-value pairs to store in this ConfigMap.
Replace theinventory.yamlfile.inventory.yaml
inventory.yaml
1apiVersion: apps.openliberty.io/v1beta2
2# tag::kind[]
3kind: OpenLibertyApplication
4# end::kind[]
5metadata:
6 name: inventory-deployment
7 labels:
8 name: inventory-deployment
9spec:
10 # tag::applicationImage[]
11 applicationImage: liberty-deepdive-inventory:1.0-SNAPSHOT
12 # end::applicationImage[]
13 service:
14 port: 9443
15 volumeMounts:
16 - name: postgres
17 # tag::mountPath[]
18 mountPath: "/config/variables/postgres"
19 # end::mountPath[]
20 readOnly: true
21 volumes:
22 - name: postgres
23 secret:
24 secretName: post-app-credentials
25 env:
26 - name: POSTGRES_HOSTNAME
27 value: "postgres"
28 - name: DEFAULT_CONTEXT_ROOT
29 valueFrom:
30 configMapKeyRef:
31 name: inv-app-root
32 key: contextRootDuring deployment, the post-app-credentials secret can be mounted to the /config/variables/postgres in the pod to create Liberty config variables. Liberty creates variables from the files in the /config/variables/postgres directory. Instead of including confidential information in the server.xml configuration file, users can access it using normal Liberty variable syntax, ${postgres/username} and ${postgres/password}.
Run the following command to deploy your changes.
kubectl apply -f inventory.yamlRun the following command to check your pods status:
kubectl get podsIf all the pods are working correctly, you see an output similar to the following example:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE inventory-deployment-75f9dc56d9-g9lzl 1/1 Running 0 35s postgres-58bd9b55c7-6vzz8 1/1 Running 0 13s
Run the following command to set up port forwarding to access the inventory microservice:
kubectl port-forward svc/inventory-deployment 9443The application might take some time to get ready. See the https://localhost:9443/health URL to confirm that the inventory microservice is up and running. You can now check out the service at the https://localhost:9443/openapi/ui/ URL. The servers dropdown list shows the https://localhost:9443/dev URL. Or, you can run the following command to access the inventory microservice:
curl -k https://localhost:9443/dev/api/systemsTearing down the environment
When you’re finished trying out the microservice, press CTRL+C in the command-line session where you ran the kubectl port-forward command to stop the port forwarding. You can delete all Kubernetes resources by running the kubectl delete commands:
kubectl delete -f inventory.yaml
kubectl delete -f ../../finish/postgres/postgres.yaml
kubectl delete configmap inv-app-root
kubectl delete secret post-app-credentialsTo uninstall the Open Liberty Operator, run the following commands:
OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=default
WATCH_NAMESPACE='""'
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenLiberty/open-liberty-operator/main/deploy/releases/1.2.1/kubectl/openliberty-app-operator.yaml \
| sed -e "s/OPEN_LIBERTY_WATCH_NAMESPACE/${WATCH_NAMESPACE}/" \
| kubectl delete -n ${OPERATOR_NAMESPACE} -f -
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenLiberty/open-liberty-operator/main/deploy/releases/1.2.1/kubectl/openliberty-app-rbac-watch-all.yaml \
| sed -e "s/OPEN_LIBERTY_OPERATOR_NAMESPACE/${OPERATOR_NAMESPACE}/" \
| kubectl delete -f -
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenLiberty/open-liberty-operator/main/deploy/releases/1.2.1/kubectl/openliberty-app-crd.yaml
kubectl delete -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.12.3/cert-manager.yamlPerform the following steps to stop your Kubernetes cluster and return your environment to a clean state.
-
Point the Docker daemon back to your local machine:
eval $(minikube docker-env -u) -
Stop your Minikube cluster:
minikube stop -
Delete your cluster:
minikube delete
Support Licensing
Open Liberty is open source under the Eclipse Public License v1 so there is no fee to use it in production. Community support is available at StackOverflow, Gitter, or the mail list, and bugs can be raised in GitHub. Commercial support is available for Open Liberty from IBM. For more information, see the IBM Marketplace. The WebSphere Liberty product is built on Open Liberty. No migration is required to use WebSphere Liberty, you simply point to WebSphere Liberty in your build. WebSphere Liberty users get support for the packaged Open Liberty function.
WebSphere Liberty is also available in Maven Central.
You can use WebSphere Liberty for development even without purchasing it. However, if you have production entitlement, you can easily change to use it with the following steps.
In the build.gradle, add the liberty element as the following:
liberty {
runtime = [ 'group':'com.ibm.websphere.appserver.runtime',
'name':'wlp-kernel']
}
Rebuild and restart the inventory service by dev mode:
./gradlew clean
./gradlew libertyDevIn the Containerfile, replace the Liberty image at the FROM statement with websphere-liberty as shown in the following example:
FROM icr.io/appcafe/websphere-liberty:full-java11-openj9-ubi ARG VERSION=1.0 ARG REVISION=SNAPSHOT ...
Great work! You’re done!
You just completed a hands-on deep dive on Liberty!
Guide Attribution
A Technical Deep Dive on Liberty by Open Liberty is licensed under CC BY-ND 4.0

Prerequisites:
Great work! You're done!
What did you think of this guide?




Thank you for your feedback!
What could make this guide better?
Raise an issue to share feedback
Create a pull request to contribute to this guide
Need help?
Ask a question on Stack Overflow



