 See all blog posts
See all blog posts
Config variables using Kubernetes secrets, installation of user features, and more exciting enhancements in Open Liberty 21.0.0.11
Open Liberty 21.0.0.11 comes with plenty of exciting improvements including Kubernetes secrets as Liberty config variables, new ways to install user features, and a new HTTP access log format option for the ephermal port of the client. This update also comes with many significant bug fixes.
In Open Liberty 21.0.0.11:
View the list of fixed bugs in 21.0.0.11.
Run your apps using 21.0.0.11
If you’re using Maven, here are the coordinates:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.openliberty</groupId>
<artifactId>openliberty-runtime</artifactId>
<version>21.0.0.11</version>
<type>zip</type>
</dependency>Or for Gradle:
dependencies {
libertyRuntime group: 'io.openliberty', name: 'openliberty-runtime', version: '[21.0.0.11,)'
}Or if you’re using Docker:
FROM open-libertyOr take a look at our Downloads page.
Using Kubernetes secrets as Liberty config variables
In a cloud environment, sensitive information such as passwords and OAuth tokens may be stored in Kubernetes secrets. To access these secrets today in Liberty via configuration variables they would need to be exposed as environment variables in a Kubernetes pod. This update will allow configuration variables to be automatically populated from Kubernetes secrets without having to expose them as environment variables.
To make use of this function, the Kubernetes secrets need to be mapped to the file system. This can be done by mounting the secrets to a volume in the pod definition, or by using a third party product to automatically handle the mapping. Files will be read from the locations defined in the VARIABLE_SOURCE_DIRS environment variable, which defaults to WLP_CONFIG_DIR/variables. The variable name will be taken from the name of the file, and the value will be the contents of the file.
For example, we may have a Kubernetes secret named 'accountdb' that contains a username and password:
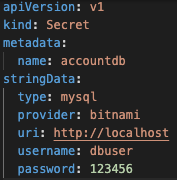
A utility such as Hashicorp’s Vault agent can automatically map that secret to the file system, or it could be done manually in a deployment definition:
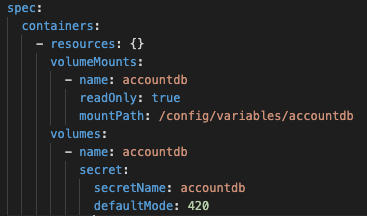
This deployment definition will result in the files /config/variables/accountdb/username and /config/variables/accountdb/password being created when the pod is created. Liberty will create variables from both files, and users can access them using normal Liberty variable syntax, ${accountdb/username} and ${accountdb/password}.
For more information visit Kubernetes Secrets or check out the Externalizing config using MicroProfile, ConfigMaps and Secrets Interactive Tutorial, which runs on Open Liberty!
Enable installation of user features on Open Liberty
You can now install user features onto the Open Liberty runtime from Maven Central or on-premises Maven repository by using the featureUtility command-line tool and the Liberty Maven and Gradle plug-ins.
Usage is as follows:
Create a features-bom (Bill of Materials) file for the user feature. The features-bom artifact in each groupId provides the bill of materials (BOM) for each Maven artifact.
<project>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>userTest.user.test.features</groupId>
<artifactId>features-bom</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<name>user features bill of materials</name>
<description>user features bill of materials</description>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>userTest.user.test.features</groupId>
<artifactId>testesa1</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<type>esa</type>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>Generate the features.json file with the Liberty Maven or Gradle plugin. The features.json file is the JSON file that contains the information from a feature’s ESA manifest file. The JSON files are a key requirement for installation of any Liberty feature from a Maven repository. Provide the Maven coordinates of the features-bom file that you created for the feature.
If you’re using Maven, use the prepare-feature goal:
<plugin>
<groupId>io.openliberty.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>liberty-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
...
<execution>
<id>prepare-feature</id>
<phase>prepare-package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-feature</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
...
</executions>
<configuration>
<installDirectory>/opt/ibm/wlp</installDirectory>
<serverName>test</serverName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>userTest.user.test.features</groupId>
<artifactId>features-bom</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>Or for Gradle, use the prepareFeature task:
dependencies {
featuresBom 'userTest.user.test.features:features-bom:1.0'
}Install the user feature using the featureUtility command-line tool, Liberty Maven or Gradle plugin. Provide the Maven coordinates of the features-bom file that you created for the feature.
| Tool | Usage |
|---|---|
|
|
Maven Plugin |
|
Gradle Plugin |
|
New HTTP access log format option for the ephemeral port of the client
When using the HTTP access log, it’s sometimes useful to print the ephemeral port of the client for each incoming HTTP request to directly correlate to network trace in a lightweight way.
Previously, the main way to correlate HTTP requests to network trace used WebContainer trace which is quite heavy. The new %{remote}p HTTP access log format option allows for a lightweight way to correlate to network trace to help investigate network errors or performance issues. A TCP socket is uniquely identified by the tuple (local IP, local port, remote IP, remote port). In the case of Liberty as an HTTP server, the client uses a local ephemeral port and this is the key to uniquely identifying the request in the network trace.
Add the %{remote}p format option to the HTTP access log configuration (<accessLogging />). For example:
<httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint" httpPort="9080" httpsPort="9443">
<accessLogging filepath="${server.output.dir}/logs/http_access.log" logFormat="%h %u %t "%r" %s %b %D %{R}W %{remote}p %p" />
</httpEndpoint>Example log entry written to http_access.log:
127.0.0.1 - [16/Aug/2021:10:42:24 -0700] "GET /swat/ HTTP/1.1" 200 21983 5625 3708 59212 9080In this example, 59212 is the client’s ephemeral port and 9080 is the Liberty HTTP port. Here is an example Wireshark network capture showing the same conversation:
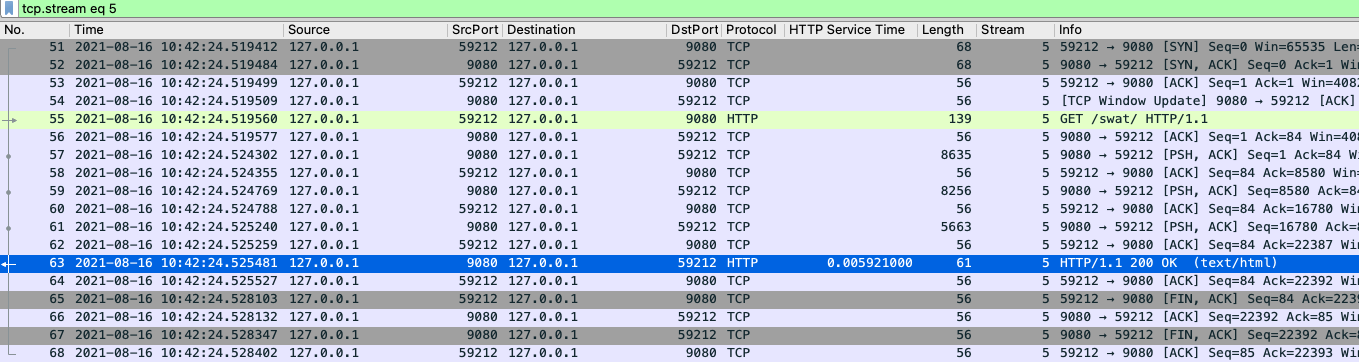
To find out more visit HTTP access logging in the Open Liberty documentation.
Notable bugs fixed in this release
We’ve spent some time fixing bugs. The following sections describe just some of the issues resolved in this release. If you’re interested, here’s the full list of bugs fixed in 21.0.0.11.
-
Fix PasswordUtil.passwordEncode() with "hash" option
Previously, the
PasswordUtilpasswordEncode()with the "hash" option was not working, as the api returned null. There was an issue with the API code where some default information needed to hash the data was not getting populated. This bug was fixed so thatPasswordUtil.passwordEncode(password, "hash")now returns a hashed string. The method was returning null due to missing information needed to create the hashed string. The default values for the missing information were not being used. -
HTTP/2 streams closed due to client window update delay
Liberty’s HTTP/2 implementation enforces a non-configurable timeout for pending writes that are waiting for a window update from the client. That is, when a stream cannot write data due to a window size limitation, then the stream waits for only the timeout period for a window update to arrive from the client. After that deadline elapses, the stream is reset. Previously, this timeout was ~8s, which is insufficient for some scenarios. Liberty should’ve waited for at least the configured
writeTimeoutperiod. This issue is now fixed. Streams that are waiting on write window updates are closed less aggressively by Liberty and streams are no longer closed before thewriteTimeoutperiod has elapsed. -
@Schema(multipleOf = ) can throw NumberFormatException in mpOpenAPI-2.0 feature
Previously, when certain non-integer numbers were used as the value for
@Schema.multipleOf, no OpenAPI documentation was produced and the following error was seen in the log:CWWKO1661E: An error occurred when processing application <application name> and an OpenAPI document was not produced. The error was: java.lang.NumberFormatException.This was caused by a bit manipulation bug in Jandex and was fixed by updating to the latest version.
-
gRPC service registration broken for EAR deployments
Previously,
gRPCservices deployed on Liberty viagrpc-1.0were not registered correctly when they were embedded in anEAR(rather than aWAR). This resulted in the services never being made available. Additionally, the followingFFDCwould be logged:Exception = com.ibm.wsspi.adaptable.module.UnableToAdaptException Source = io.openliberty.grpc.internal.servlet.GrpcServerComponent probeid = 230 Stack Dump = com.ibm.wsspi.adaptable.module.UnableToAdaptException: CWWKM0453E: WebSphere Application Server internal error occurred. Please contact WebSphere Application Server support with the following data: Container is not a module com.ibm.ws.adaptable.module.internal.InterpretedContainerImpl@1e2a2e4f ( <app_location_and_name> ) at com.ibm.ws.container.service.annocache.internal.WebAnnotationsAdapterImpl.adapt(WebAnnotationsAdapterImpl.java:54) at com.ibm.ws.container.service.annocache.internal.WebAnnotationsAdapterImpl.adapt(WebAnnotationsAdapterImpl.java:33) at com.ibm.ws.adaptable.module.internal.AdapterFactoryServiceImpl.adapt(AdapterFactoryServiceImpl.java:200) at com.ibm.ws.adaptable.module.internal.AdaptableContainerImpl.adapt(AdaptableContainerImpl.java:174) at com.ibm.ws.adaptable.module.internal.InterpretedContainerImpl.adapt(InterpretedContainerImpl.java:203) at com.ibm.ws.container.service.annocache.AnnotationsBetaHelper.getWebAnnotations(AnnotationsBetaHelper.java:268) at io.openliberty.grpc.internal.servlet.GrpcServerComponent.initServicesHelper(GrpcServerComponent.java:243) ...This issue has now been resolved, meaning that the
gRPCservices should start as expected and noFFDCshould be logged. -
SAML JSP gets unexpected 500 error due to ClassCastException
Previously, the SAML JSP would get an unexpected 500 error, as a ClassCastException was returned instead of a normal SAML error during certain SAML SSO login errors. The issue was caused by a 'jarentry' being handled by the wrong classload processor. However, this issue has now been fixed and it will now be handled by the correct bundle processor. Note that 'jar' types are still handled correctly.
-
ServletContainerInitializer is passed invalid @HandlesTypes classes
@HandlesTypes is used on a ServletContainerInitializer to specify classes which should be passed to its
onStartup(java.util.Set<java.lang.Class<?>>, javax.servlet.ServletContext)at application startup time. Liberty correctly includes the implementations of the@HandlesTypesclasses - however if a class specified in the@HandlesTypesparameter is not defined via@interfacethen it will also be included in theonStartupset. This issue fixed the problem where the@interfaceannotation was not used in the@HandlesTypesso that the specify classes can be passed into theonStartup(). The usage is as follows:public interface MyInterface { ... } public MyInterfaceImpl implements MyInterface @HandlesTypes({MyInterface.class}) public class MyServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> scanResult, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException { // scanResult should contain all implementations of MyInterface; // current Liberty will pass in: // { MyInterfaceImpl.class } // {MyInterface} should NOT be passed into onStartup } }The above can also be written using annotation format:
public @interface MyInterface @MyInterface public MyInterfaceImpl -
Previously, ExpressionFactory#getClassNameServices(ClassLoader tccl) failed when
META-INF/services/javax.el.ExpressionFactorydid not contain a qualified class name in its first line. This was a problem with the el-3.0 implementation, and was fixed by porting over the patch in BZ 64097. -
Liberty message.log has repeating servlet lifecycle messages
The following messages appeared many times in the Liberty log for certain apps that used JSP with a TLD file, beginning with 21.0.0.7.
SRVE0242I: [ ... ] Initialization successful. SRVE0253I: [ ... ] Destroy successful.Each time a JSP is accessed, if included files have been updated since last compile it causes a new JSP compile. This would cause the message:
SRVE0253I: [ … ] Destroy successful. The issue is that aTLDfile under/WEB-INFin theWARwasn’t being checked correctly, causing it to appear to always be out of date, therefore causing the JSP to compile every time it is accessed and resulting in aSRVE0253I. In a heavily used app, theSRVE0253Imight have caused excessive logging due to the frequency of its occurrence. The issue happened when the following was set:<applicationManager autoExpand="false"/>`. This issue has now been fixed, meaning that in the above scenario SRVE0253I does not occur.
Get Open Liberty 21.0.0.11 now
Available through Maven, Gradle, Docker, and as a downloadable archive.





