 See all blog posts
See all blog posts
Simplify observability with MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 and more in 24.0.0.9
In this release, MicroProfile Telemetry standardizes the observability of your Java applications by using OpenTelemetry to collect and export logs, metrics, and traces. The release also includes a solution for managing third-party browser cookies and new additions to our versionless features collection.
In Open Liberty 24.0.0.9:
View the list of fixed bugs in 24.0.0.9.
Check out previous Open Liberty GA release blog posts.
Develop and run your apps using 24.0.0.9
If you’re using Maven, include the following code in your pom.xml file:
<plugin>
<groupId>io.openliberty.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>liberty-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.10.3</version>
</plugin>Or for Gradle, include the following in your build.gradle file:
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'io.openliberty.tools:liberty-gradle-plugin:3.8.3'
}
}
apply plugin: 'liberty'Or if you’re using container images:
FROM icr.io/appcafe/open-libertyOr take a look at our Downloads page.
If you’re using IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio Code or Eclipse IDE, you can also take advantage of our open source Liberty developer tools to enable effective development, testing, debugging, and application management all from within your IDE.
Manage your logs, metrics, and traces with MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0
In this release, the MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 feature (mpTelemetry-2.0) helps improve the observability of your Java applications by using OpenTelemetry to collect and export logs, metrics, and traces in a standardized way. Previous versions of MicroProfile Telemetry could manage only distributed tracing.
For more information about the available configuration properties, see MicroProfile Config properties: MicroProfile Telemetry.
For more information about using MicroProfile Telemetry to manage your metrics, logs, and traces in a standardized way, see Enable observability with MicroProfile Telemetry.
MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 provides the latest OpenTelemetry technology. In addition to distributed tracing, the feature now allows OpenTelemetry to collect and export metrics and logs. For information about managing metrics and logs with MicroProfile Telemetry, see the following sections.
Send Liberty metrics to OpenTelemetry
When the MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 feature (mpTelemetry-2.0) is enabled, Open Liberty can now forward runtime component statistics that are captured by the Performance Monitoring 1.0 feature (monitor-1.0) to the MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 runtime. This statistical data is registered as metrics in the telemetry runtime and can be forwarded to any OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP) compatible metric consumer to meet your monitoring needs.
The following runtime components are supported:
-
ThreadPool -
Sessions -
RequestTiming -
ConnectionPool
To collect and export metrics, enable OpenTelemetry by using the following system property or environment variable:
-
System property:
otel.sdk.disabled=false -
Environment variable:
OTEL_SDK_DISABLED=false
You can set configuration properties in any of the config sources that are available to MicroProfile Config.
Enable the mpTelemetry-2.0 feature and any features that are associated with your chosen supported runtime components. The mpTelemetry-2.0 feature automatically enables the monitor-1.0 feature.
For example, the ConnectionPool component requires the following configuration:
<featureManager>
<feature>mpTelemetry-2.0</feature>
<feature>jdbc-4.3</feature>
</featureManager>By default, all OpenTelemetry data is exported to OTLP. You can set a different exporter by specifying the following system property or environment variable:
-
System property:
otel.metrics.exporter -
Environment variable:
OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER
You can also optionally configure the metric export interval configuration variable. The value is specified in milliseconds and the default is 60000 (60 seconds).
-
System property:
otel.metric.export.interval -
Environment variable:
OTEL_METRIC_EXPORT_INTERVAL
For more information about the available configuration properties, see MicroProfile Config properties: MicroProfile Telemetry.
Send logs to OpenTelemetry
The mpTelemetry-2.0 feature can now collect Open Liberty runtime log sources (messages, traces, ffdcs) and application logs generated through the java.util.logging (JUL) package.
To enable the MicroProfile Telemetry 2.0 feature to collect all logs, add the following configuration to your server.xml file:
<featureManager>
<feature>mpTelemetry-2.0</feature>
</featureManager>
<mpTelemetry source="message, trace, ffdc"/>If the mpTelemetry configuration element or the source attribute is not configured, the message source is set by default. In this case, only messages are collected. If the source attribute is specified empty (source=""), no logs are sent to OpenTelemetry.
To collect and export runtime-level logs, enable OpenTelemetry by using the following system property or environment variable:
-
System property:
otel.sdk.disabled=false -
Environment variable:
OTEL_SDK_DISABLED=false
You can set configuration properties in any of the config sources that are available to MicroProfile Config.
To separately configure multiple applications in a server, you can configure OpenTelemetry with application configuration. However, you cannot collect runtime-level logs this way.
By default, all OpenTelemetry data is exported to OTLP. You can set a different exporter by specifying the following system property or environment variable:
-
System property:
otel.logs.exporter -
Environment variable:
OTEL_LOGS_EXPORTER
For more information about the available configuration properties, see MicroProfile Config properties: MicroProfile Telemetry.
Keep using third-party cookies with CHIPS
To increase privacy and reduce tracking, Google Chrome announced it would phase out third-party cookies in 2025. Then, as of July 22, 2024, Chrome stated they might scrap the phase-out plan due to regulatory concerns. Users could instead opt to block third-party cookies via their browser. Some sites that are designed with third-party cookies in mind are broken by browsers that opt-in to block third-party cookies. Chrome provides documentation to help you test whether your sites are affected. If you are, one option to mitigate this change is called CHIPS: Cookies Having Independent Partitioned State.
First, some background information regarding third-party (cross-site) cookies.
If a top-level site X embeds another site Z, such as an iframe, then any cookies set by the embedded site Z might be shared with any other site that embeds site Z, such as top-level site Y. This vulnerability is due to cookies placed in a cookie jar under the Z site key. This scenario assumes that the cookie is labeled as SameSite=None, because it isn’t shared when set to Lax or Strict.
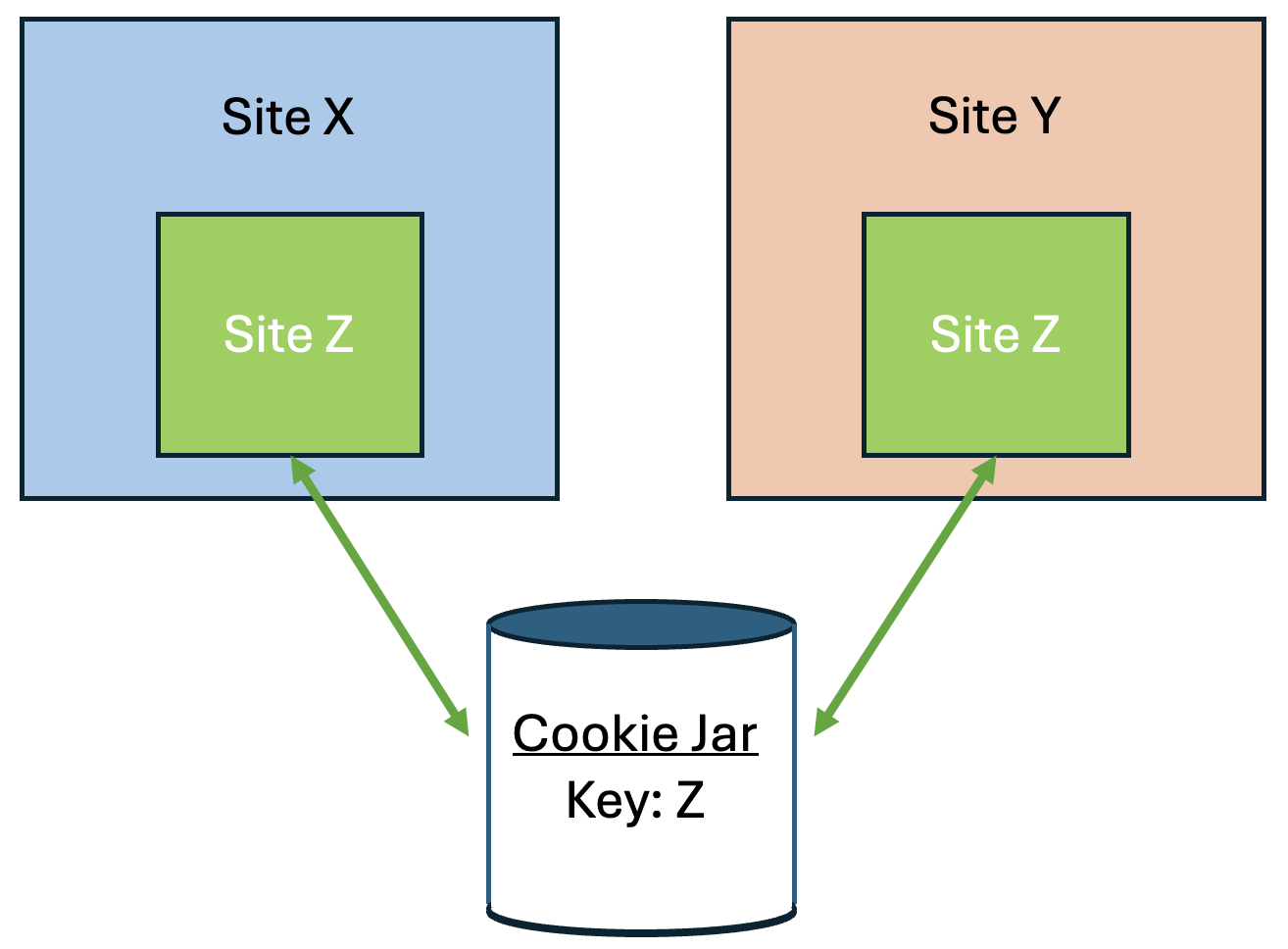
Chrome provides a Partitioned cookie attribute, which divides the cookie jar, as a workaround for third-party cookies with limitations. Instead of saving the cookies within the Z site key, they are also keyed under the top-level site, such as X and Y. In this way, if X embeds Z and Y embeds Z, the Z’s cookies will not be shared between X and Y.
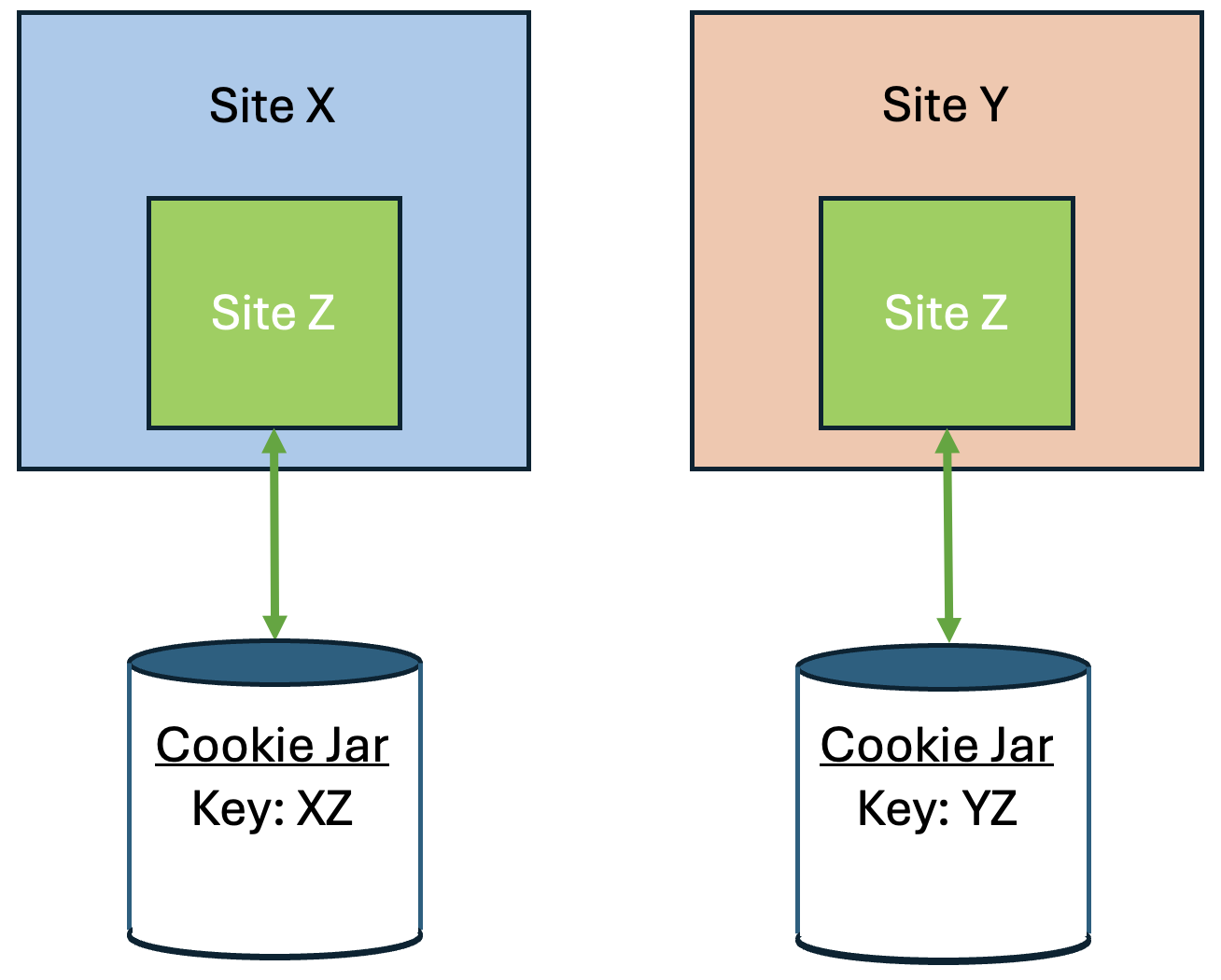
You can use the Partitioned attribute to specify whether a cookie is partitioned. If the SameSite=None attribute is missing from the cookie, it is blocked by Chrome and any Chromium-based browsers because it is treated as Lax.
The partitioned attribute configuration is opt-in and behaves much like the SameSite configuration. The samesite channel configuration applies to all cookies, while the httpSession and webAppSecurity configurations apply to their respective cookies. It’s important to note that the httpSession and webAppSecurity configurations take precedence over the channel configuration. The default value for these two attributes is defer, which means they defer to the channel configuration. As for channel configuration, its default value is false, which means the Partitioned attribute is not added.
Depending on which configuration you use to declare the Partitioned attribute, Liberty uses one of three attributes.
The following example shows how to set the cookiePartitioned attribute for the HTTP session cookie on the httpSession attribute in your server.xml file:
<httpSession cookieSameSite="None" cookiePartitioned="defer|true|false"/>`The following example shows how to set the partitionedCookie attribute for LTPA and JWT security cookies on the webAppSecurity attribute in your server.xml file:
<webAppSecurity sameSiteCookie="None" partitionedCookie="defer|true|false"/>`The following example shows how to set the partitioned attribute for other cookies on the httpEndpoint attribute in your server.xml file:
<httpEndpoint id="defaultHttpEndpoint"
httpPort="9080"
httpsPort="9443" >
<samesite none="*" partitioned="true|false"/>
</httpEndpoint>Alternatively, you can set Partitioned by using the Set-Cookie header with the following two HttpServletResponse APIs:
For more information, including a visual example, see CHIPS (Cookies Having Independent Partitioned State) on GitHub.
Versionless features for Java / Jakarta EE Container Liberty features
In 24.0.0.8, Open Liberty introduced versionless Java EE and Jakarta EE features. Those new versionless features allow you to easily use features without needing to know what feature version to use. The initial release of versionless features did not include the Container features, which enable you to provide your own implementation of certain Java EE or Jakarta EE component specifications. An example of such a feature is facesContainer-4.0.
In 24.0.0.9, Open Liberty adds versionless features for the missing Container features. The following versionless features are added:
-
jpaContainer/persistenceContainer -
jsfContainer/facesContainer -
jsonbContainer -
jsonpContainer
The following server.xml configuration file uses the Java EE platform javaee-8.0 with versionless features jpaContainer, jsfContainer, jsonbContainer, and jsonpContainer:
<!-- Enable features -->
<featureManager>
<platform>javaee-8.0</platform>
<feature>jpaContainer</feature>
<feature>jsfContainer</feature>
<feature>jsonbContainer</feature>
<feature>jsonpContainer</feature>
</featureManager>Learn more and check out the full collection of available platforms and versionless features in the Open Liberty docs. Stay tuned for more versionless features and platforms in future releases.
Security vulnerability (CVE) fixes in this release
| CVE | CVSS Score | Vulnerability Assessment | Versions Affected | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
5.3 |
Information disclosure |
17.0.0.3 - 24.0.0.8 |
For a list of past security vulnerability fixes, reference the Security vulnerability (CVE) list.
Get Open Liberty 24.0.0.9 now
Available through Maven, Gradle, Docker, and as a downloadable archive.





