 See all blog posts
See all blog posts
Deploy Java applications to IBM Cloud Code Engine using the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty
You can use IBM Cloud Code Engine to easily deploy Java applications by using the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty with your container images or source code.
This post provides instructions on how to use the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty with Code Engine. To learn more about using Code Engine, see Getting started with IBM Cloud Code Engine.
IBM Cloud announced the deprecation of Cloud Foundry. Code Engine provides the next level of easy application deployment and mature management of critical business applications in IBM Cloud. Move your applications from the Cloud Foundry liberty-for-java buildpack to a cloud native solution using Code Engine and the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty.
What do you need?
-
An IBM Cloud Account
-
Your application source
To deploy container images, you’ll also need:
-
The pack CLI
-
Docker or Podman. This post focuses on Docker. For information about using Podman with Paketo, refer to the buildpacks.io documentation for Building on Podman.
-
An externally accessible container registry that can host your images.
For details on deploying your application from repository source code from the Code Engine console, see Code Engine console.
For details on deploying your application from repository source code with the CLI, see CLI.
Code Engine build strategies
Code Engine can build your container from source with Paketo buildpacks using the Cloud Native Buildpacks build strategy. The Paketo Buildpack for Liberty is included in the composite Paketo Buildpack for Java that also includes tomcat and tomee application servers. Tomcat is the default application server and to use Open Liberty requires a little extra configuration.
You can set the application server that the Paketo Buildpack for Java uses by specifying the BP_JAVA_APP_SERVER environment variable. If this variable is undefined, the order of Java application servers in the buildpack dictates which one will be picked. Normally, environment variables are provided to buildpacks by using the --env parameter on the pack build CLI command. However, Code Engine does not use pack, so the environment variables must be provided in a .buildenv file in the application’s root source directory.
Let’s get started
Create the .buildenv file in the application’s root source directory. At a minimum, .buildenv should contain BP_JAVA_APP_SERVER=liberty but can contain other environment variables consumed by buildpacks.
BP_JAVA_APP_SERVER=libertyLog in to the IBM Cloud console and head to the Code Engine overview page. When you are building from source, enter the URL of the repository that hosts your source and click Start creating .
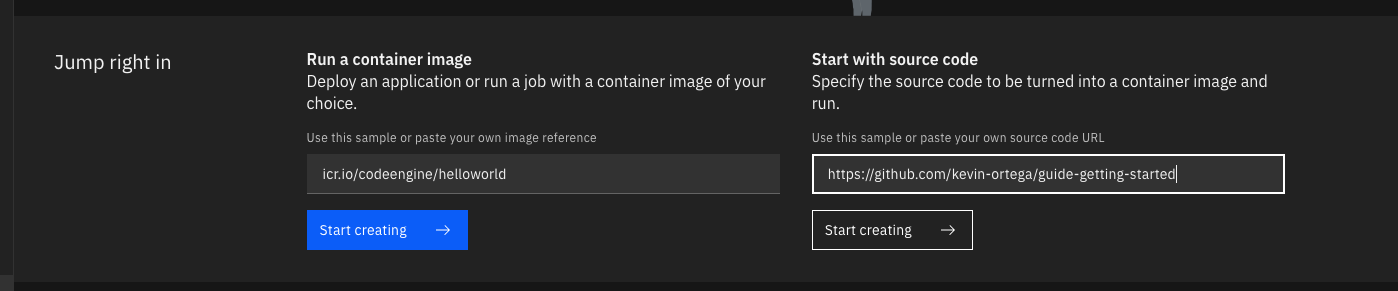
On the Start creating page, you must enter 9080 as the value for Listening port.
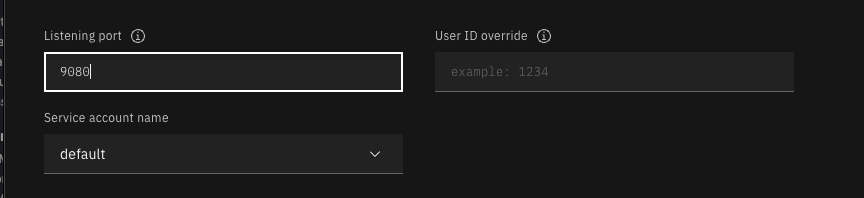
In the Runtime settings section, we recommend setting the minimum number of instances to 1.
Click Specify build details.
In this example, the source root that contains the .buildenv file is the finish directory.
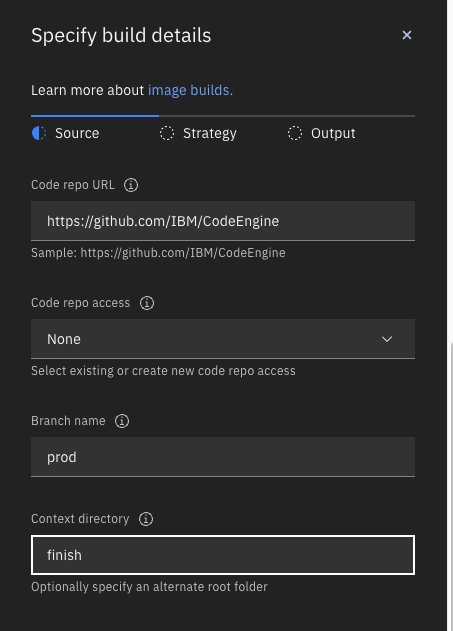
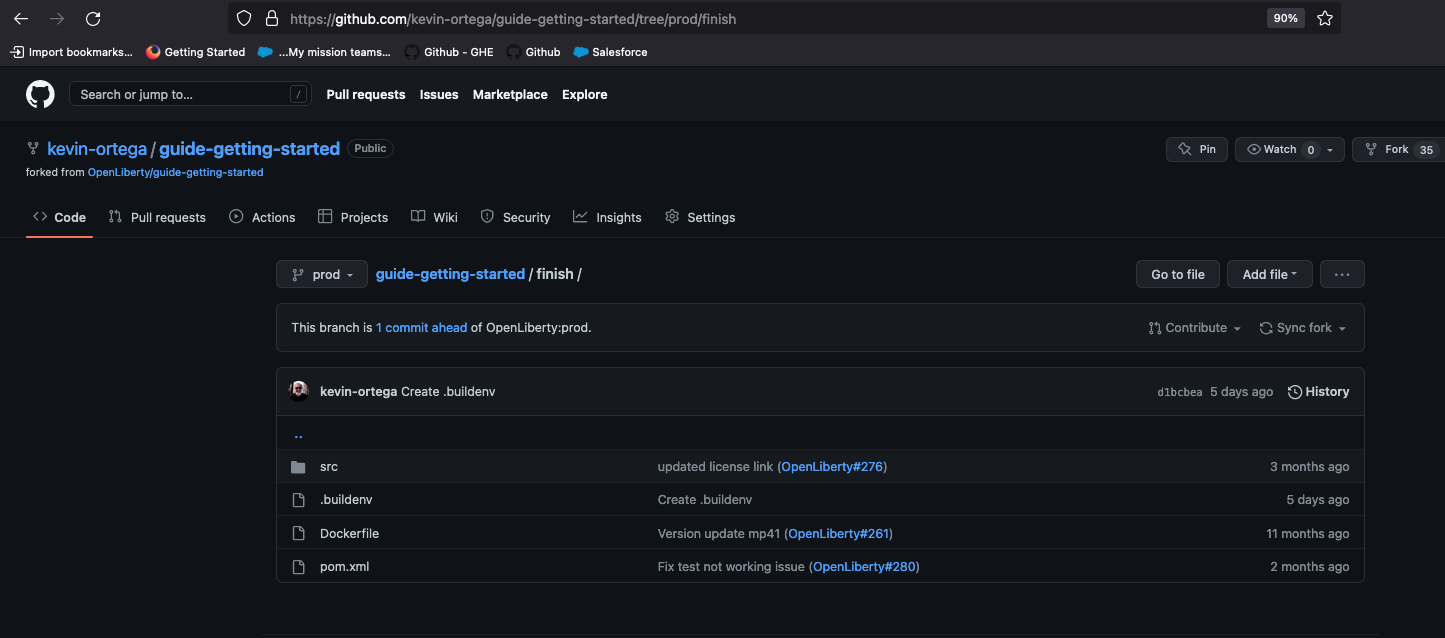
Click Next and select Cloud Native Buildpack as the source. Click Next.
Enter the details of where Code Engine will store your image and click Done.
Click Create to have Code Engine create and deploy your application.
The Build step details output will show the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty contributed to the image.
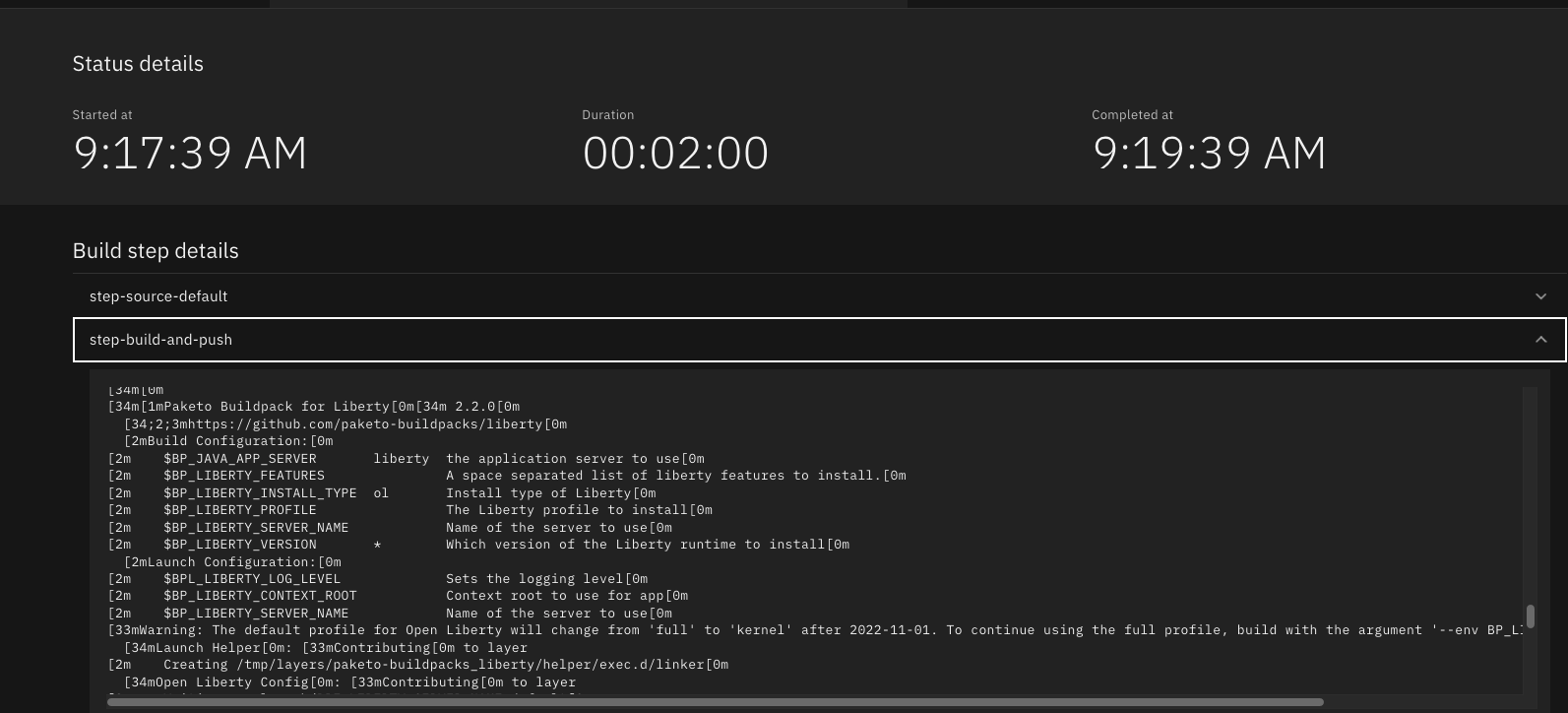
Similarly, if you’re creating your application from source using the Code Engine CLI you need to specify the port and build strategy along with the .buildenv file present in the application source root directory:
$ ibmcloud ce app create --name MYAPPNAME --image REGISTRY/NAMESPACE/REPOSITORY --registry-secret SECRET --build-source . --strategy buildpacks --port 9080
[finish (prod=)]$ ls -la
total 24
drwxr-xr-x 7 kevin staff 224 Oct 28 14:54 .
drwxr-xr-x 12 kevin staff 384 Oct 19 11:07 ..
-rw-r--r--@ 1 kevin staff 26 Nov 4 12:53 .buildenv
-rw-r--r-- 1 kevin staff 790 Oct 19 11:07 Dockerfile
-rw-r--r--@ 1 kevin staff 4066 Oct 19 11:07 pom.xml
drwxr-xr-x 4 kevin staff 128 Oct 19 11:07 src
drwxr-xr-x 11 kevin staff 352 Oct 20 08:53 target-
Create a
.buildenvfile that defines theBP_JAVA_APP_SERVER=libertyenvironment variable. -
Set the listening port to 9080
Other environment variables you can set in the .buildenv file
- BP_LIBERTY_INSTALL_TYPE
-
Specifies the Install type of Liberty. Open Liberty (value of
ol) is the default. - BP_LIBERTY_PROFILE
-
Specifies which liberty profile to install. Valid profiles for Liberty are documented in the buildpacks documentation.
- BP_LIBERTY_FEATURES
-
Specifies a space-separated list of Liberty features to be installed with the Liberty runtime. Supports any valid Liberty feature.
Taking full advantage of all what the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty has to offer
Code Engine doesn’t use the pack build CLI to create container images. It plugs into the cloud native buildpack’s lifecycle natively. As a result, some features of the Paketo Buildpack for Liberty are not easily available to Code Engine. Features like installing iFixes, custom features, and installing from a packaged server or server directory aren’t available when you use Code Engine to create the container image.
For these features, you can use the pack build CLI to create the container image, push the image to an external container registry. Then, use Code Engine to deploy and manage your container by pulling your container image from the container registry from the Code Engine console or CLI.
Follow these instructions to deploy applications from the IBM Cloud Container Registry with Code Engine.




