 See all blog posts
See all blog posts
Fast iterative development of multi-module Maven projects with dev mode
You can organize a cloud-native Java application that is built with Maven by separating it into multiple subprojects, or modules. A multi-module project consists of multiple modules that can have dependencies on each other and an aggregator project that describes how the modules are built together. The Maven reactor then collects, sorts, and builds the modules in the correct order.
In this blog post, we introduce support for working with multi-module Maven projects in Open Liberty dev mode. Dev mode for multi-module projects provides hot deployment of changes in all modules of a Maven reactor build, on-demand and hot testing for multiple modules, and the ability to attach a debugger to debug code in any module.
Dev mode support for multi-module Maven projects is available starting in version 3.4 of the Liberty Maven plug-in, which you can use now.
Multi-module projects
With multi-module Maven projects, a top-level aggregator pom.xml file manages a group of modules. You can run a single command to build the entire project, and the Maven reactor determines the correct build order for you.
The following example is the Open Liberty multi-module sample application. This project contains three modules: a Java library in the jar folder, a web module in the war folder, and template files and the Open Liberty server configuration in the ear folder.
guide-maven-multimodules
|_ pom.xml
|_ jar
|_pom.xml
|_src/main/java
|_ war
|_pom.xml
|_src/main
|_java
|_webapp
|_ ear
|_pom.xml
|_src
|_main/liberty/config
|_test/java
Each module is defined in the top-level aggregator pom.xml file:
<modules>
<module>jar</module>
<module>war</module>
<module>ear</module>
</modules>The modules within the project can also have dependencies on each other. In this example, the war module depends on the jar module, and the ear module depends on both the war and jar modules. With dev mode for multiple modules, the code changes you make are automatically picked up and hot deployed and any dependent modules are also recompiled and hot deployed.
Running a multi-module project with Open Liberty dev mode
You can run a multi-module project on Open Liberty with a single command by using dev mode or dev mode with container support. To use any of these options, you must first define the Liberty Maven plug-in.
Defining the Liberty Maven plug-in
To use the Liberty Maven plug-in in your multi-module project, you can define the plug-in in either the parent pom.xml file of every module or in the pom.xml of every module.
For example, if your modules have a <parent> element that points to a parent project, add the Liberty Maven plug-in to the <pluginManagement> section of the parent project’s pom.xml as follows:
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>io.openliberty.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>liberty-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.4</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>Starting dev mode
To start dev mode, run the following command from the directory that contains the top-level multi-module pom.xml:
mvn liberty:dev
Once dev mode starts successfully, changes in all modules are detected and hot deployed. By default, any dependent modules are also recompiled and deployed. For example, if you make a change in the jar module of the previously described sample application, the war module is also recompiled because it depends on the jar module.
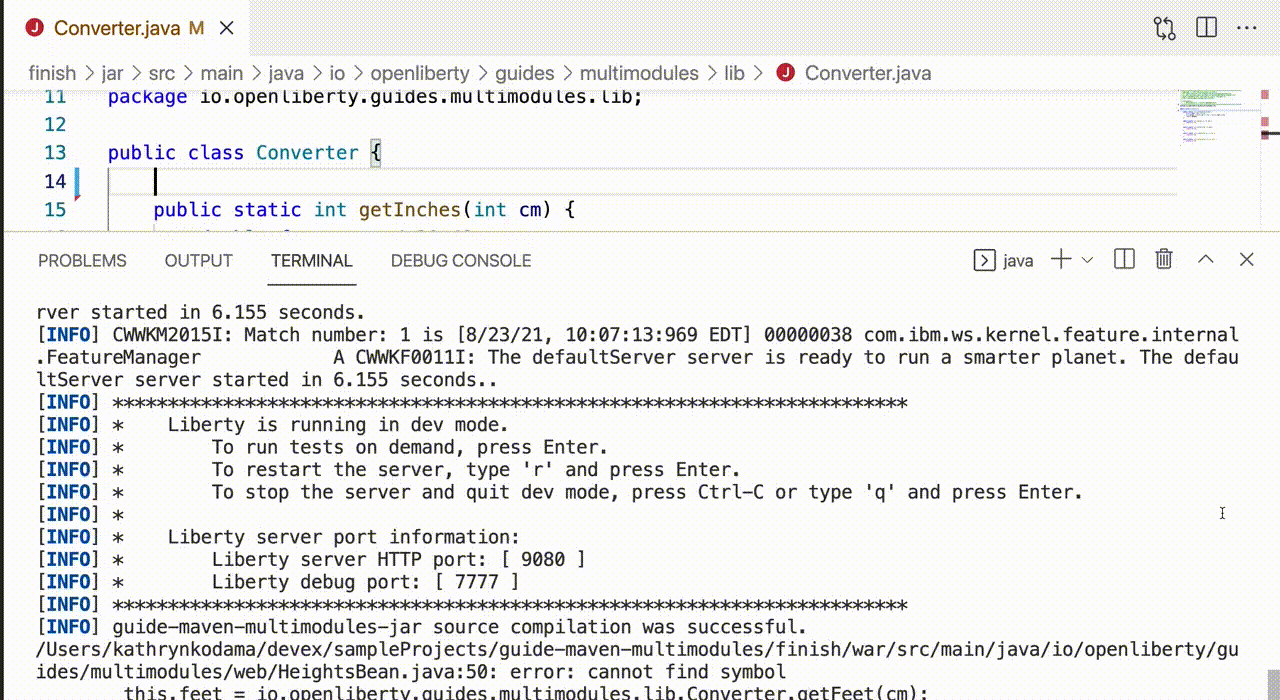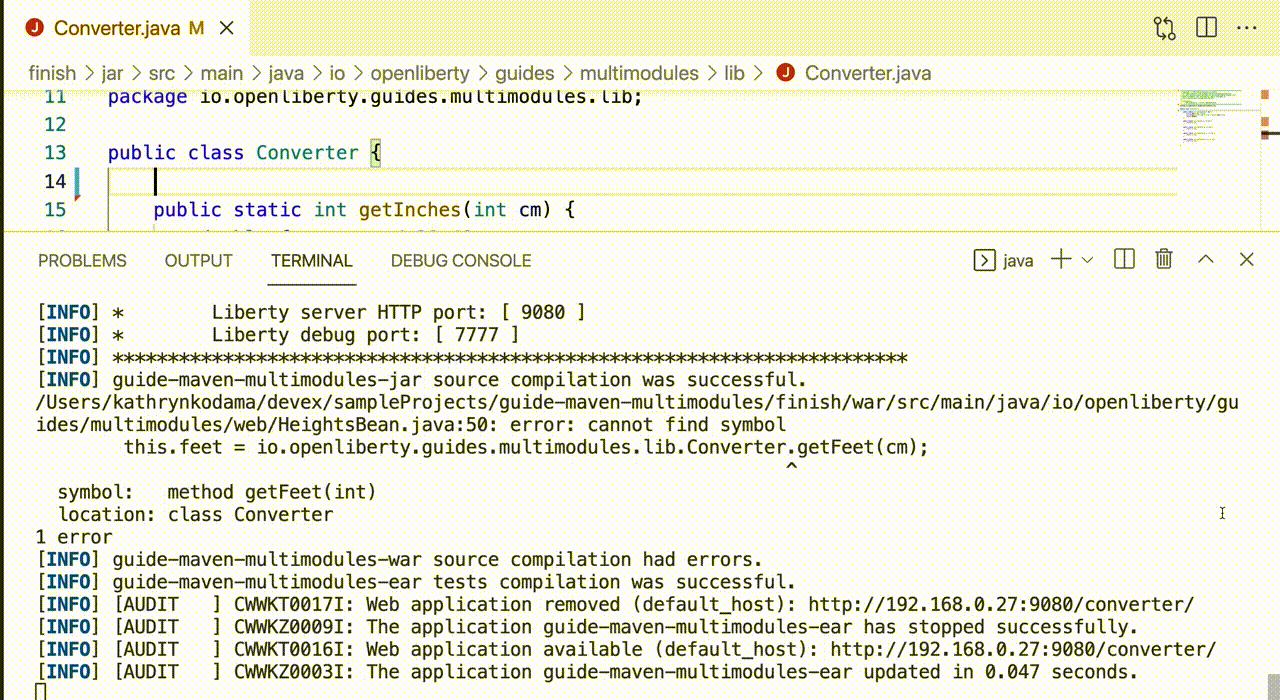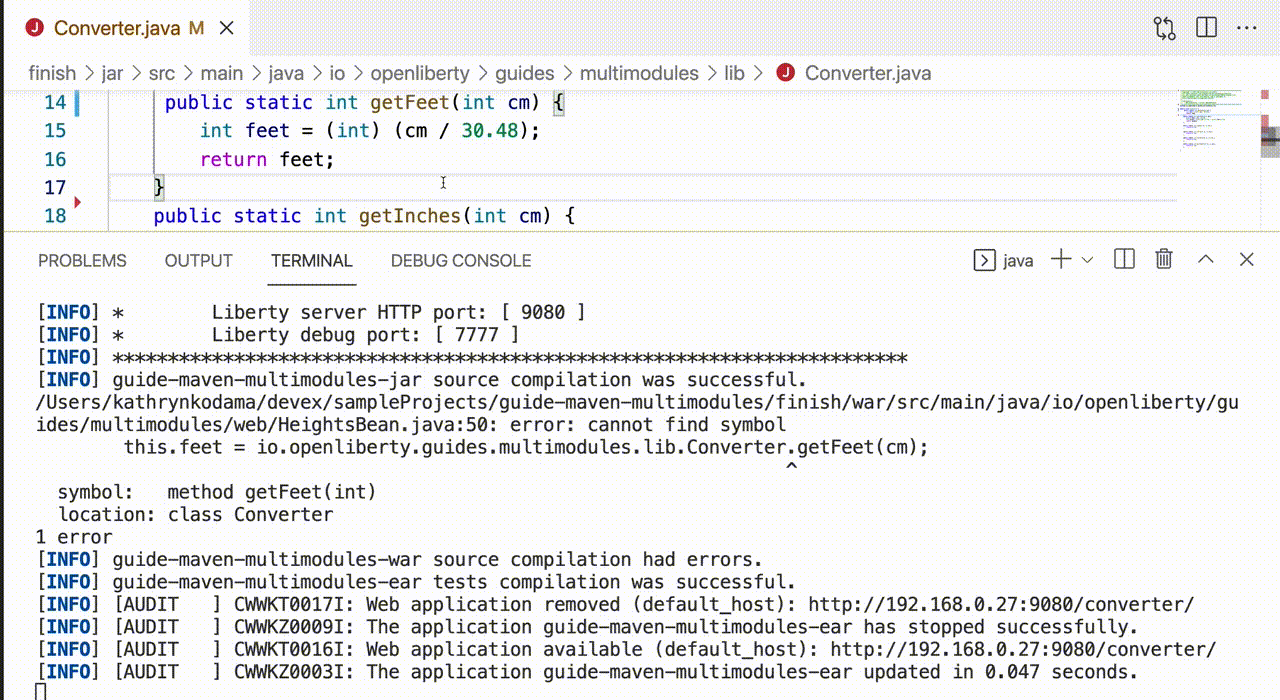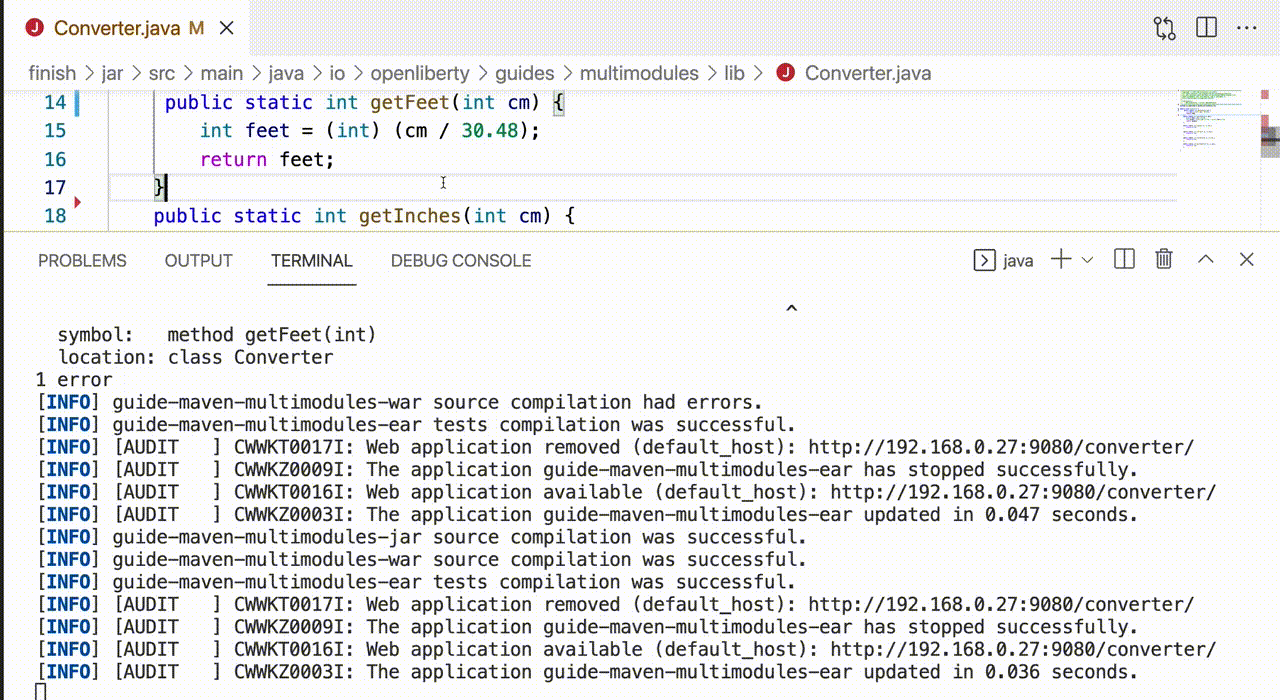
Starting dev mode with container support
Dev mode with container support is available for multi-module projects. Use the devc goal to start dev mode with container support:
mvn liberty:devc
If your Dockerfile is not in the same directory as where you started the dev mode command from, you can point to it with the -Ddockerfile=<path-to-dockerfile> command parameter. For more information on Dockerfiles for your Open Liberty application, see the Open Liberty Docker image documentation.
Running tests
You can run tests on all modules by pressing Enter for immediate feedback on your code changes.
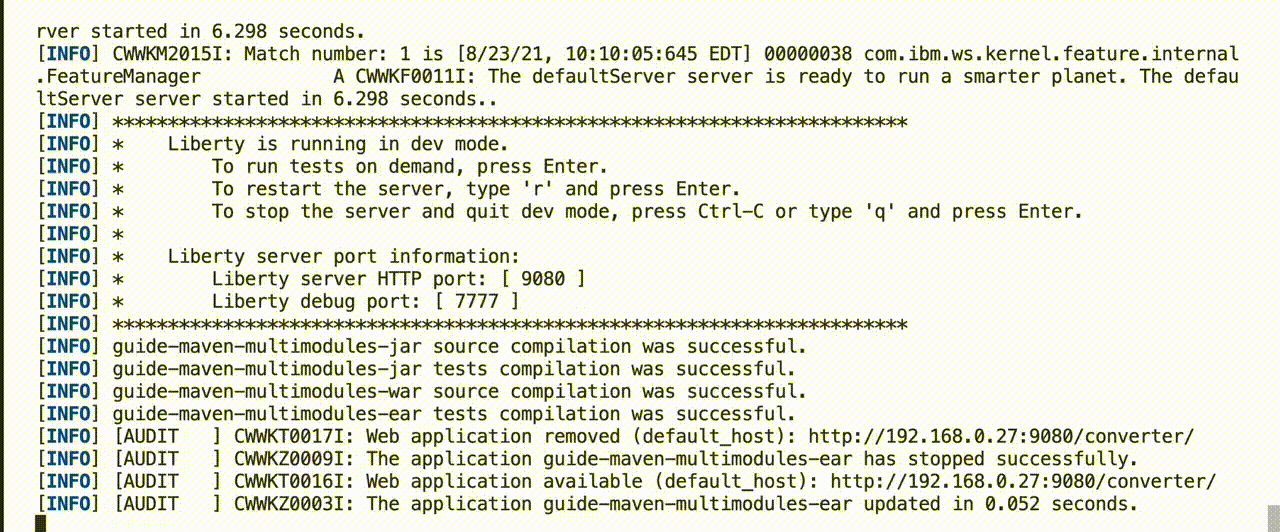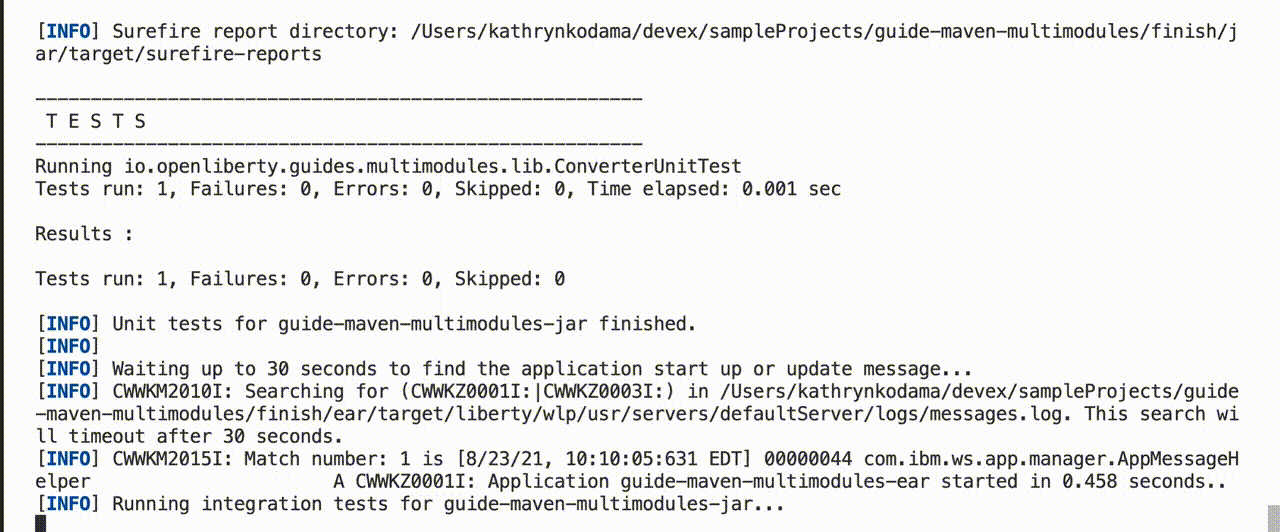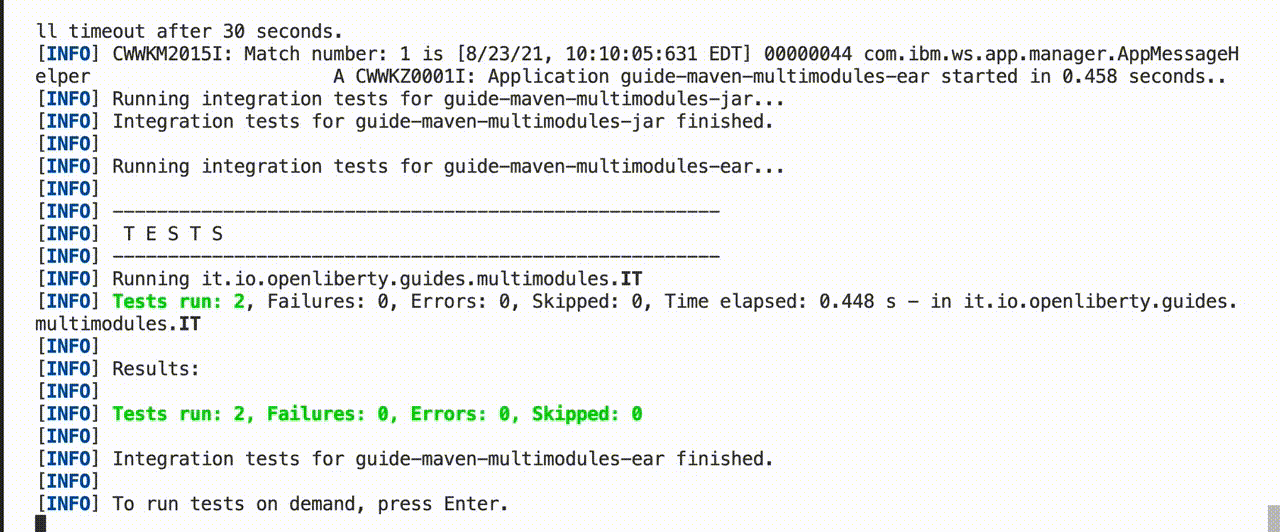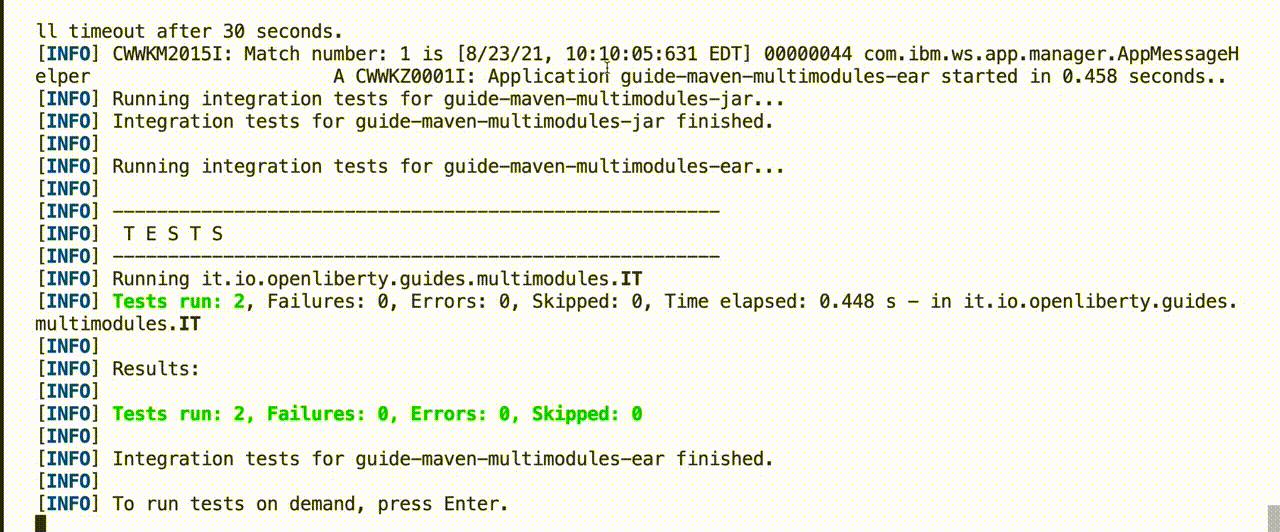
You can also enable hot tests, which run on every code change. To enable hot tests, add the -DhotTests parameter to your dev or devc command: mvn liberty:dev -DhotTests. When hot tests are enabled, tests run on the module that was changed and any dependent modules.
Attaching a debugger
You can attach a debugger to the running server to step through your code at any time. You can specify breakpoints in any module’s source code to locally debug different parts of your application. The default port for debugging is 7777.
Stopping dev mode
To exit dev mode, press Control+C or type q in the terminal and press Enter.
Additional resources
For more details on how to use dev mode with multi-module projects, see the documentation for multiple modules in the Liberty Maven plug-in’s dev goal.




